The immunoregulatory protein B7-H3 promotes aerobic glycolysis in oral squamous carcinoma via PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway
- PMID: 31737114
- PMCID: PMC6843865
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.29838
The immunoregulatory protein B7-H3 promotes aerobic glycolysis in oral squamous carcinoma via PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway
Abstract
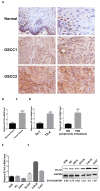
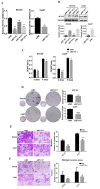
OSCC (oral squamous carcinoma) is one of most common malignant cancer. Although previous studies have found abnormal expression of B7-H3 in human OSCC, the exact role and molecular mechanism of B7-H3 in OSCC remain unknown. In this study, we investigated the role of B7-H3 in glucose metabolic reprogramming of OSCC cells in vitro and in vivo. We first detected the expression of B7-H3 in OSCC samples. Next, siRNAs and overexpression short-hairpin RNA of B7-H3 were transfected into SCC25 and Cal27 cells, and cell proliferation, migration and invasion were analyzed via CCK8, colony formation and transwell assays. Then glycolysis flux was determined through measuring glucose uptake and lactate production, and mRNA and protein expression levels were determined by real-time quantitative PCR and western blot respectively. The results presented here showed B7-H3 was upregulated in OSCC samples compared with normal tissues, and the expression level was associated with tumor size and nodal metastasis. B7-H3 affects OSCC cell proliferation, migration and invasion. We also found that B7-H3 promoted the Warburg effect, evidenced by increase glucose uptake and lactate production. We further demonstrated that B7-H3 enhanced OSCC glycolysis through the upregulation of HIF-1α and its downstream targets, Glut1 and PFKFB3, which are key factors in glycolysis. Mechanically, we demonstrated that B7-H3 regulates HIF-1α expression through PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Metabolic imaging of human OSCC cancer xenograft in mice confirmed that B7-H3 enhanced tumor glucose uptake, glycolysis promoted genes expression and tumor growth. Taken together, our results have unveiled a mechanism that B7-H3 drives OSCC progression through enhancing of glycolytic metabolic program in OSCC.
Keywords: B7-H3; OSCC; PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway; glycolysis; immunoregulatory protein.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures





References
-
- Siegel R L, Miller K D, Dvm A J. Cancer statistics, 2017[J] Ca A Cancer J for Clinicians. 2017;67:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Warnakulasuriya S. Global epidemiology of oral and oropharyngeal cancer. Oral Oncol. 2009;45:309–316. - PubMed
-
- Feng Z, Xu Q, Chen W. Epigenetic and genetic alterations-based molecular classification of head and neck cancer. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2012;12:279–290. - PubMed
-
- Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ, He J. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:115–132. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

