Presymptomatic Retinal Sensitivity Changes in Intermediate Age-Related Macular Degeneration Associated With New Retinal Fluid
- PMID: 31737427
- PMCID: PMC6855368
- DOI: 10.1167/tvst.8.6.3
Presymptomatic Retinal Sensitivity Changes in Intermediate Age-Related Macular Degeneration Associated With New Retinal Fluid
Abstract
Purpose: To determine whether change in retinal sensitivity in areas with subretinal or intraretinal fluid secondary to age-related macular degeneration (AMD) precedes visual symptoms. If confirmed, retinal sensitivity testing could be used for home monitoring in AMD.
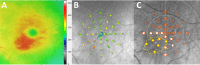
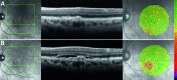
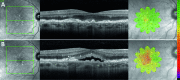
Methods: Individuals with intermediate AMD enrolled in a longitudinal study were seen every 6 months and underwent best-corrected visual acuity testing (BCVA), spectral domain-optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT), and microperimetry. Asymptomatic individuals who developed incidental, reading center-determined retinal fluid detected on SD-OCT were identified. The point-wise sensitivity (PWS) at the time of fluid detection was compared with 6 and 12 months prior.
Results: Fourteen of 161 individuals developed fluid without symptoms. PWS over fluid areas at detection was reduced compared with 6 (difference -2.04 dB, P < 0.001) and 12 months (-2.27 dB, P < 0.001) prior. PWS over fluid areas was reduced compared with perifluid areas (difference -1.02 dB, P = 0.03), peripheral areas (-1.51 dB, P < 0.001), nonprogressed fellow eyes (-1.49 dB, P = 0.006), and nonprogressed age-matched intermediate AMD eyes (-2.29 dB, P = 0.001). No difference in BCVA was observed in eyes developing fluid compared to eyes that do not develop fluid (P = 0.76).
Conclusions: Retinal areas with fluid on SD-OCT had a corresponding reduction in retinal sensitivity at the time of fluid detection compared with 6 and 12 months prior, in asymptomatic intermediate AMD without change in BCVA.
Translational relevance: Development of self-monitoring tools to detect changes in retinal sensitivity may be helpful for early detection of retinal fluid suggestive of progression to neovascular AMD before acuity is affected.
Keywords: SD-OCT; age-related macular degeneration; microperimetry; retinal fluid; retinal sensitivity.
Copyright 2019 The Authors.
Figures


References
-
- Bloch SB, Larsen M, Munch IC. Incidence of legal blindness from age-related macular degeneration in Denmark: year 2000 to 2010. Am J Ophthalmol. 2012;153:209–213. e202. - PubMed
-
- Fong DS, Custis P, Howes J, Hsu J-W. Intravitreal bevacizumab and ranibizumab for age-related macular degeneration: a multicenter, retrospective study. Ophthalmology. 2010;117:298–302. - PubMed
-
- Olsen TW, Feng X, Kasper TJ, Rath PP, Steuer ER. Fluorescein angiographic lesion type frequency in neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmology. 2004;111:250–255. - PubMed
-
- Finger RP, Wickremasinghe SS, Baird PN, Guymer RH. Predictors of anti-VEGF treatment response in neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Surv Ophthalmol. 2014;59:1–18. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

