Tropomyosin receptor kinase (TRK) biology and the role of NTRK gene fusions in cancer
- PMID: 31738427
- PMCID: PMC6859819
- DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdz383
Tropomyosin receptor kinase (TRK) biology and the role of NTRK gene fusions in cancer
Abstract
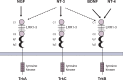
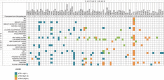
The tropomyosin receptor kinase (TRK) family of receptor tyrosine kinases are encoded by NTRK genes and have a role in the development and normal functioning of the nervous system. Since the discovery of an oncogenic NTRK gene fusion in colorectal cancer in 1986, over 80 different fusion partner genes have been identified in a wide array of adult and paediatric tumours, providing actionable targets for targeted therapy. This review describes the normal function and physiology of TRK receptors and the biology behind NTRK gene fusions and how they act as oncogenic drivers in cancer. Finally, an overview of the incidence and prevalence of NTRK gene fusions in various types of cancers is discussed.
Keywords: NTRK gene fusions; TRK; TRK fusion cancer; tropomyosin receptor kinase.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society for Medical Oncology.
Figures


References
-
- Weier HU, Rhein AP, Shadravan F. et al. Rapid physical mapping of the human trk protooncogene (NTRK1) to human chromosome 1q21-q22 by P1 clone selection, fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), and computer-assisted microscopy. Genomics 1995; 26(2): 390–393. - PubMed
-
- Nakagawara A, Liu XG, Ikegaki N. et al. Cloning and chromosomal localization of the human TRK-B tyrosine kinase receptor gene (NTRK2). Genomics 1995; 25(2): 538–546. - PubMed
-
- Valent A, Danglot G, Bernheim A.. Mapping of the tyrosine kinase receptors trkA (NTRK1), trkB (NTRK2) and trkC(NTRK3) to human chromosomes 1q22, 9q22 and 15q25 by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Eur J Hum Genet 1997; 5(2): 102–104. - PubMed
-
- Skaper SD. The biology of neurotrophins, signalling pathways, and functional peptide mimetics of neurotrophins and their receptors. CNS Neurol Discord Drug Targets 2008; 7(1): 46–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

