CAR T-cell therapy is effective for CD19-dim B-lymphoblastic leukemia but is impacted by prior blinatumomab therapy
- PMID: 31738832
- PMCID: PMC6880911
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2019000692
CAR T-cell therapy is effective for CD19-dim B-lymphoblastic leukemia but is impacted by prior blinatumomab therapy
Abstract
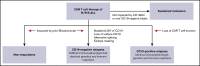
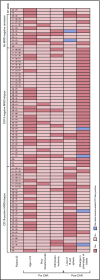
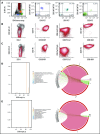
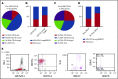
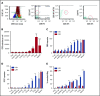
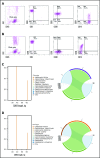
Tisagenlecleucel, a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell product targeting CD19 is approved for relapsed/refractory B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL). However, the impact of pretreatment variables, such as CD19 expression level, on leukemic blasts, the presence of CD19- subpopulations, and especially prior CD19-targeted therapy, on the response to CAR T-cell therapy has not been determined. We analyzed 166 patients treated with CAR T-cell therapy at our institution. Eleven patients did not achieve a minimal residual disease (MRD)- deep remission, whereas 67 patients had a recurrence after achieving a MRD- deep remission: 28 patients with CD19+ leukemia and 39 patients with CD19- leukemia. Return of CD19+ leukemia was associated with loss of CAR T-cell function, whereas CD19- leukemia was associated with continued CAR T-cell function. There were no significant differences in efficacy of CAR T cells in CD19-dim B-ALL, compared with CD19-normal or -bright B-ALL. Consistent with this, CAR T cells recognized and lysed cells with very low levels of CD19 expression in vitro. The presence of dim CD19 or rare CD19- events by flow cytometry did not predict nonresponse or recurrence after CAR T-cell therapy. However, prior therapy with the CD19-directed, bispecific T-cell engager blinatumomab was associated with a significantly higher rate of failure to achieve MRD- remission or subsequent loss of remission with antigen escape. Finally, immunophenotypic heterogeneity and lineage plasticity were independent of underlying clonotype and cytogenetic abnormalities.
© 2019 by The American Society of Hematology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: S.L.M. is a consultant/advisory board member for Novartis Pharmaceutical Corporation (NPC) and Kite Pharma. S.A.G. has received research and/or clinical trial support from NPC, Servier, and Kite and has served as consultant for and on study steering committees or scientific/clinical advisory boards of NPC, Cellectis, Adaptimmune, Eureka, TCR2, Juno, GlaxoSmithKline, Vertex, Cure Genetics, Humanigen, and Roche. C.H.J. reports receiving research funding from NPC and Immune Design and is a consultant/advisory board member for NPC, Tmunity Therapeutics, and Immune Design. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- von Stackelberg A, Locatelli F, Zugmaier G, et al. . Phase I/Phase II Study of Blinatumomab in Pediatric Patients With Relapsed/Refractory Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(36):4381-4389. - PubMed
-
- Teachey DT, Hunger SP. Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in 2017: immunotherapy for ALL takes the world by storm. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2018;15(2):69-70. - PubMed

