Near Real-Time Surveillance to Assess the Safety of the 9-Valent Human Papillomavirus Vaccine
- PMID: 31740498
- PMCID: PMC7780202
- DOI: 10.1542/peds.2019-1808
Near Real-Time Surveillance to Assess the Safety of the 9-Valent Human Papillomavirus Vaccine
Abstract
Background and objectives: Human papillomavirus is the most common sexually transmitted infection in the United States and causes certain anogenital and oropharyngeal cancers. The 9-valent human papillomavirus vaccine (9vHPV) provides protection against additional types not included in the quadrivalent vaccine. We conducted near real-time vaccine safety surveillance for 24 months after the vaccine became available in the Vaccine Safety Datalink.
Methods: Immunizations and adverse events were extracted weekly from October 2015 to October 2017 from standardized data files for persons 9 to 26 years old at 6 Vaccine Safety Datalink sites. Prespecified adverse events included anaphylaxis, allergic reaction, appendicitis, Guillain-Barré syndrome, chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy, injection site reaction, pancreatitis, seizure, stroke, syncope, and venous thromboembolism. The observed and expected numbers of events after 9vHPV were compared weekly by using sequential methods. Both historical and concurrent comparison groups were used to identify statistical signals for adverse events. Unexpected signals were investigated by medical record review and/or additional analyses.
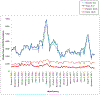
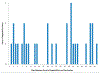
Results: During 105 weeks of surveillance, 838 991 doses of 9vHPV were administered. We identified unexpected statistical signals for 4 adverse events: appendicitis among boys 9 to 17 years old after dose 3; pancreatitis among men 18 to 26 years old; and allergic reactions among girls 9 to 17 years old and women 18 to 26 years old after dose 2. On further evaluation, which included medical record review, temporal scan analysis, and additional epidemiological analyses, we did not confirm signals for any adverse events.
Conclusions: After 2 years of near real-time surveillance of 9vHPV and several prespecified adverse events, no new safety concerns were identified.
Copyright © 2019 by the American Academy of Pediatrics.
Conflict of interest statement
POTENTIAL CONFLICT OF INTEREST: Dr Naleway has received funding from Pfizer for an unrelated study; Dr Klein reports research support from Merck (including a 9-valent human papillomavirus vaccine phase 4 postmarketing safety study), Sanofi Pasteur, GlaxoSmithKline, Protein Science (now Sanofi Pasteur), and Pfizer; the other authors have indicated they have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Comment in
-
From Peyton Rous to the HPV Vaccine: A Journey of Discovery and Progress.Pediatrics. 2019 Dec;144(6):e20192345. doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-2345. Epub 2019 Nov 18. Pediatrics. 2019. PMID: 31740499 No abstract available.
References
-
- Markowitz LE, Dunne EF, Saraiya M, et al.; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Human papillomavirus vaccination: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR Recomm Rep. 2014;63(RR):1–30 - PubMed
-
- Markowitz LE, Dunne EF, Saraiya M, et al.; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC); Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). Quadrivalent human papillomavirus vaccine: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR Recomm Rep. 2007;56(RR):1–24 - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Recommendations on the use of quadrivalent human papillomavirus vaccine in males–Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP), 2011. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2011;60(50):1705–1708 - PubMed
-
- Petrosky E, Bocchini JA Jr, Hariri S, et al.; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Use of 9-valent human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine: updated HPV vaccination recommendations of the advisory committee on immunization practices. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2015;64(11):300–304 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

