Single Hepatocyte Hepatitis B Virus Transcriptional Landscape in HIV Coinfection
- PMID: 31740931
- PMCID: PMC7137881
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiz607
Single Hepatocyte Hepatitis B Virus Transcriptional Landscape in HIV Coinfection
Abstract
Background: Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a leading cause of liver failure and hepatocellular carcinoma. Approximately 10% of people with HIV also have HBV and are at higher risk of liver disease progression than in HBV monoinfection. Antivirals, common to HIV and HBV, suppress HBV DNA levels but do not eradicate virus because the transcriptional template, covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA), is long lived in infected hepatocytes.
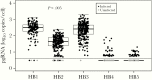
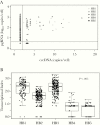
Methods: Using single-cell laser capture microdissection, we isolated >1100 hepatocytes from 5 HIV/HBV coinfected persons with increasing exposure to HBV antivirals (HB1-HB5; no exposure to >7 years exposure), quantifying cccDNA and pregenomic RNA (pgRNA) in each cell using droplet digital polymerase chain reaction.
Results: The proportion of infected hepatocytes decreased with antiviral exposure from 96.4% (HB1) to 29.8% (HB5). Upper cccDNA range and median pgRNA decreased from HB1 to HB5 (P < .05 for both). The amount of pgRNA transcribed per cccDNA also decreased from HB1 to HB5 (P < .05). Cells with inactive pgRNA transcription were enriched from 0% (HB1) to 14.3% (HB5) of infected hepatocytes.
Conclusions: cccDNA transcription is reduced in HIV/HBV coinfected people with longer antiviral duration. Understanding HBV transcriptional regulation may be critical to develop a functional cure.
Keywords: HBV transcription; HIV/HBV coinfection; intrahepatic hepatitis B; single-cell laser capture microdissection; viral landscape; viroscape.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For permissions, e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures


References
-
- Rustgi VK, Hoofnagle JH, Gerin JL, et al. . Hepatitis B virus infection in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Intern Med 1984; 101:795–7. - PubMed
-
- Homann C, Krogsgaard K, Pedersen C, Andersson P, Nielsen JO. High incidence of hepatitis B infection and evolution of chronic hepatitis B infection in patients with advanced HIV infection. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 1991; 4:416–20. - PubMed
-
- Thio CL, Seaberg EC, Skolasky R Jr, et al. ; Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study HIV-1, hepatitis B virus, and risk of liver-related mortality in the Multicenter Cohort Study (MACS). Lancet 2002; 360:1921–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

