Effect of quercetin on oxidative stress and liver function in beta-thalassemia major patients receiving desferrioxamine: A double-blind randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 31741663
- PMCID: PMC6856539
- DOI: 10.4103/jrms.JRMS_911_18
Effect of quercetin on oxidative stress and liver function in beta-thalassemia major patients receiving desferrioxamine: A double-blind randomized clinical trial
Abstract
Background: Blood transfusion therapy is lifesaving for beta-thalassemia major patients, yet it indirectly causes complications such as oxidative stress and liver dysfunction. In the present study, we investigated the effect of quercetin supplementation on oxidative stress and liver function in beta-thalassemia major patients.
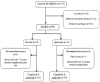
Materials and methods: In this double-blind clinical trial, 84 beta-thalassemia patients who received desferrioxamine (DFO) were randomly assigned to two groups; the treatment group received 500 mg quercetin tablet daily for 12 weeks, and the control group received placebo. In addition to demographic and anthropometric assessment, malondialdehyde (MDA), total antioxidant capacity (TAC), superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) were biochemically assessed to detect the effect of quercetin on oxidative stress and liver function, respectively. The data were analyzed using SPSS 21. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results: Before adjusting for confounding variables, within-group comparison showed that quercetin supplementation reduced ALT (P < 0.001) and TAC (P < 0.001) significantly. Between-group comparison using analysis of covariance analysis though showed that quercetin could significantly reduce ALT (P = 0.002), but there was an insignificant increase in SOD and TAC, and insignificant decrease in GPx, MDA, AST, and ALP (P > 0.05).
Conclusion: According to our results, consumption of 500 mg quercetin supplement daily for 3 months along with DFO treatment might be able to alter liver function, but not the oxidative stress in beta-thalassemia major patients.
Keywords: Beta-thalassemia; liver; oxidative stress; quercetin.
Copyright: © 2019 Journal of Research in Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effect of aqueous extract of Iranian oak (Quercus brantii) on antioxidant capacity and oxidative stress in beta-thalassemia patients: Randomized controlled trial.Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2024 Jun;61:230-236. doi: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2024.03.037. Epub 2024 Apr 4. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2024. PMID: 38777439 Clinical Trial.
-
Quercetin attenuates lindane induced oxidative stress in Wistar rats.Mol Biol Rep. 2012 Jun;39(6):6895-905. doi: 10.1007/s11033-012-1516-0. Mol Biol Rep. 2012. PMID: 22302394
-
The impact of silymarin on antioxidant and oxidative status in patients with β-thalassemia major: A crossover, randomized controlled trial.Complement Ther Med. 2017 Dec;35:25-32. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2017.08.007. Epub 2017 Aug 24. Complement Ther Med. 2017. PMID: 29154063 Clinical Trial.
-
An investigation of the effects of curcumin on iron overload, hepcidin level, and liver function in β-thalassemia major patients: A double-blind randomized controlled clinical trial.Phytother Res. 2018 Sep;32(9):1828-1835. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6118. Epub 2018 May 28. Phytother Res. 2018. PMID: 29806132 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of Pharmacologic Dose of Resveratrol Supplementation on Oxidative/Antioxidative Status Biomarkers in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Patients: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial.Adv Pharm Bull. 2018 Jun;8(2):307-317. doi: 10.15171/apb.2018.036. Epub 2018 Jun 19. Adv Pharm Bull. 2018. PMID: 30023333 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The effects of iron overload, insulin resistance and oxidative stress on metabolic disorders in patients with β- thalassemia major.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2020 Jun 3;19(2):767-774. doi: 10.1007/s40200-020-00560-x. eCollection 2020 Dec. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2020. PMID: 33520802 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemicals: Targeting Mitophagy to Treat Metabolic Disorders.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Aug 3;9:686820. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.686820. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34414181 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus KLDS 1.0207 Exerts Antimicrobial and Cytotoxic Effects in vitro and Improves Blood Biochemical Parameters in vivo Against Notable Foodborne Pathogens.Front Microbiol. 2020 Sep 24;11:583070. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.583070. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33072056 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rund D, Rachmilewitz E. Beta-thalassemia. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:1135–46. - PubMed
-
- Jomova K, Valko M. Importance of iron chelation in free radical-induced oxidative stress and human disease. Curr Pharm Des. 2011;17:3460–73. - PubMed
-
- Rachmilewitz EA, Giardina PJ. How I treat thalassemia. Blood. 2011;118:3479–88. - PubMed
-
- Lee KW, Kim YJ, Kim DO, Lee HJ, Lee CY. Major phenolics in apple and their contribution to the total antioxidant capacity. J Agric Food Chem. 2003;51:6516–20. - PubMed
-
- Bischoff SC. Quercetin: Potentials in the prevention and therapy of disease. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2008;11:733–40. - PubMed