Distantly Related Rotaviruses in Common Shrews, Germany, 2004-2014
- PMID: 31742508
- PMCID: PMC6874240
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2512.191225
Distantly Related Rotaviruses in Common Shrews, Germany, 2004-2014
Abstract
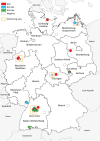
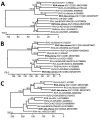
We screened samples from common shrews (Sorex araneus) collected in Germany during 2004-2014 and identified 3 genetically divergent rotaviruses. Virus protein 6 sequence similarities to prototype rotaviruses were low (64.5% rotavirus A, 50.1% rotavirus C [tentative species K], 48.2% rotavirus H [tentative species L]). Shrew-associated rotaviruses might have zoonotic potential.
Keywords: Germany; Sorex araneus; common shrew; diarrheal disease; enteric infections; epidemiology; next-generation sequencing; phylogeny; rotavirus; rotavirus A; rotavirus C; rotavirus H; shrews; tentative species; virus diversity; viruses; zoonoses.
Figures
References
-
- Tate JE, Burton AH, Boschi-Pinto C, Parashar UD; World Health Organization–Coordinated Global Rotavirus Surveillance Network. Global, regional, and national estimates of rotavirus mortality in children <5 years of age, 2000–2013. Clin Infect Dis. 2016;62(Suppl 2):S96–105. 10.1093/cid/civ1013 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Attoui H, Mertens PPC, Becnel J, Belaganahalli S, Bergoin M, Brussaard CP, et al. Family: Reoviridae. In: King AMQ, Adams MJ, Carstens EB, Lefkowitz EJ, editors. Virus taxonomy: ninth report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. Amsterdam: Elsevier Academic Press; 2012. p. 541–637.
-
- International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. Taxonomic information. Virus taxonomy: 2018b release. 2018. Jul [cited 2019 Aug 21]. https://talk.ictvonline.org/taxonomy
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

