Nationwide survey of endogenous hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia in Japan (2017-2018): Congenital hyperinsulinism, insulinoma, non-insulinoma pancreatogenous hypoglycemia syndrome and insulin autoimmune syndrome (Hirata's disease)
- PMID: 31742894
- PMCID: PMC7232294
- DOI: 10.1111/jdi.13180
Nationwide survey of endogenous hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia in Japan (2017-2018): Congenital hyperinsulinism, insulinoma, non-insulinoma pancreatogenous hypoglycemia syndrome and insulin autoimmune syndrome (Hirata's disease)
Abstract
Aims/introduction: We aimed to investigate the nationwide incidence, treatment details and outcomes of patients with endogenous hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia (EHH), including those with transient/persistent congenital hyperinsulinism (CHI), insulinoma, non-insulinoma pancreatogenous hypoglycemia syndrome and insulin autoimmune syndrome (Hirata's disease) in Japan.
Materials and methods: A nationwide, questionnaire-based survey was carried out to determine the number of patients with EHH who were treated for hypoglycemia or hypoglycemia-related complications in 2017-2018. The questionnaires were sent to all hospitals in Japan with >300 beds, and with pediatric and/or adult clinics likely managing EHH patients. The secondary questionnaires were sent to obtain the patients' date of birth, sex, age at onset, treatment details and post-treatment outcomes.
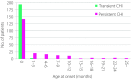
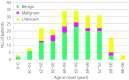
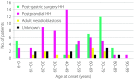
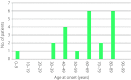
Results: A total of 447 patients with CHI (197 transient CHI, 225 persistent CHI and 25, unknown histology), 205 with insulinoma (118 benign, 18 malignant and 69 unknown subtype), 111 with non-insulinoma pancreatogenous hypoglycemia syndrome (33 post-gastric surgery HH, 57 postprandial HH, 10 nesidioblastosis and 11 unknown subtype) and 22 with insulin autoimmune syndrome were identified. Novel findings included: (i) marked improvement in the prognosis of persistent CHI over the past 10 years; (ii) male dominance in the incidence of transient CHI; (iii) non-insulinoma pancreatogenous hypoglycemia syndrome emerging as the second most common form of EHH in adults; (iv) frequent association of diabetes mellitus with insulin autoimmune syndrome; and (v) frequent post-treatment residual hypoglycemia and impaired quality of life.
Conclusions: The first nationwide, all age group survey of EHH showed the current status of each type of EHH disorder and the unmet needs of the patients.
Keywords: Hyperinsulinism; Hypoglycemia; Surveys.
© 2019 The Authors. Journal of Diabetes Investigation published by Asian Association for the Study of Diabetes (AASD) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Cryer PE. Symptoms of hypoglycemia, thresholds for their occurrence, and hypoglycemia unawareness. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 1999; 28: 495–500. - PubMed
-
- Service FJ, Natt N, Thompson GB, et al Noninsulinoma pancreatogenous hypoglycemia: a novel syndrome of hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia in adults independent of mutations in Kir6.2 and SUR1 genes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1999; 84: 1582–1589. - PubMed
-
- Hirata Y, Ishizu H, Ouchi N, et al Insulin autoimmunity in a case of spontaneous hypoglycemia. J Jpn Diabetes Soc 1970; 13: 312–320. (Japanese).
-
- Service FJ, Vella A Noninsulinoma pancreatogenous hypoglycemia syndrome. In UpToDate® Available from: http://www.uptodate.com. Accessed August 11, 2019.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

