Biomarkers for diagnosis of Wilson's disease
- PMID: 31743430
- PMCID: PMC6953362
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD012267.pub2
Biomarkers for diagnosis of Wilson's disease
Abstract
Background: Wilson's disease, first described by Samuel Wilson in 1912, is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder resulting from mutations in the ATP7B gene. The disease develops as a consequence of copper accumulating in affected tissues. There is no gold standard for the diagnosis of Wilson's disease, which is often delayed due to the non-specific clinical features and the need for a combination of clinical and laboratory tests for diagnosis. This delay may in turn affect clinical outcome and has implications for other family members in terms of diagnosis. The Leipzig criteria were established to help standardise diagnosis and management. However, it should be emphasised that these criteria date from 2003, and many of these have not been formally evaluated; this review examines the evidence behind biochemical testing for Wilson's disease.
Objectives: To determine the diagnostic accuracy of three biochemical tests at specified cut-off levels for Wilson's disease. The index tests covered by this Cochrane Review are caeruloplasmin, 24-hour urinary copper and hepatic copper content. These tests were evaluated in those with suspected Wilson's disease and appropriate controls (either healthy or those with chronic liver disease other than Wilson's). In the absence of a gold standard for diagnosing Wilson's disease, we have used the Leipzig criteria as a clinical reference standard. To investigate whether index tests should be performed in all individuals who have been recommended for testing for Wilson's disease, or whether these tests should be limited to subgroups of individuals.
Search methods: We identified studies by extensive searching of, e.g. the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), PubMed, Embase, the Web of Science and clinical trial registries (29 May 2019). Date of the most recent search of the Cochrane Cystic Fibrosis and Genetic Disorders Inborn Errors of Metabolism Register: 29 May 2019.
Selection criteria: We included prospective and retrospective cohort studies that assessed the diagnostic accuracy of an index test using the Leipzig criteria as a clinical reference standard for the diagnosis of Wilson's disease.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently reviewed and extracted data and assessed the methodological quality of each included study using the QUADAS-2 tool. We had planned to undertake meta-analyses of the sensitivity, specificity at relevant cut-offs for each of the biochemical tests for Wilson's, however, due to differences in the methods used for each biochemical index test, it was not possible to combine the results in meta-analyses and hence these are described narratively.
Main results: Eight studies, involving 5699 participants (which included 1009 diagnosed with Wilson's disease) were eligible for inclusion in the review. Three studies involved children only, one adults only and the four remaining studies involved both children and adults. Two evaluated participants with hepatic signs and six with a combination of hepatic and neurological signs and symptoms of Wilson's disease, as well as pre-symptomatic individuals. The studies were of variable methodological quality; with high risk if bias for participant selection and the reference standard used being of greatest methodological concern. Key differences between studies include differences in assay methodology, different cut-off values for diagnostic thresholds, different age and ethnicity groups. Concerns around study design imply that diagnostic accuracy figures may not transfer to populations outside of the relevant study.
Index test: caeruloplasmin Five studies evaluated various thresholds of caeruloplasmin (4281 participants, of which 541 had WD). For caeruloplasmin a cut-off of 0.2 g/L as in the Leipzig criteria achieved a sensitivity of 77.1% to 99%, with variable specificity of 55.9% to 82.8%. Using the cut-off of 0.1 g/L of the Leipzig criteria seemed to lower the sensitivity overall, 65% to 78.9%, while increasing the specificity to 96.6% to 100%.
Index test: hepatic copper Four studies evaluated various thresholds of hepatic copper (1150 participants, of which 367 had WD). The hepatic copper cut-off of 4 μmol/g used in the Leipzig criteria achieved a sensitivity of 65.7% to 94.4%, with a variable specificity of 52.2% to 98.6%.
Index test: 24-hour urinary copper Three studies evaluated various thresholds of 24-hour urinary copper (268 participants, of which 101 had WD). For 24-hour urinary copper, a cut-off of 0.64 to 1.6 μmol/24 hours used in the Leipzig criteria achieved a variable sensitivity of 50.0% to 80.0%, with a specificity of 75.6% to 98.3%.
Authors' conclusions: The cut-offs used for caeruloplasmin, 24-hour urinary copper and hepatic copper for diagnosing Wilson's disease are method-dependent and require validation in the population in which such index tests are going to be used. Binary cut-offs and use of single-test strategies to rule Wilson's disease in or out is not supported by the evidence in this review. There is insufficient evidence to inform testing in specific subgroups, defined by age, ethnicity or clinical subgroups.
Copyright © 2019 The Cochrane Collaboration. Published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Aidan Ryan: none known. Sarah Nevitt: none known. Orla Tuohy: none known. Paul Cook: none known.
Figures





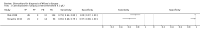

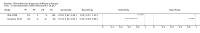
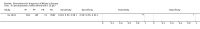
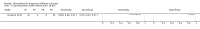


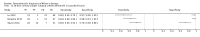

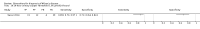
Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Ferenci 2005 {published data only}
-
- Ferenci P, Steindl‐Munda P, Vogel W, Jessner W, Gschwantler M, Stauber R, et al. Diagnostic value of quantitative hepatic copper determination in patients with Wilson's Disease. Clinical Gastroenterology & Hepatology 2005;3(8):811‐8. - PubMed
Lu 2010 {published data only}
-
- Lu Y, Liu XQ, Wang XH, Wang JS. The reassessment of the diagnostic value of 24‐hour urinary copper excretion in children with Wilson's disease. Chinese Journal of Hepatology 2010;18(1):49‐53. - PubMed
Mak 2008 {published data only}
-
- Mak CM, Lam CW, Tam S. Diagnostic accuracy of serum ceruloplasmin in Wilson disease: determination of sensitivity and specificity by ROC curve analysis among ATP7B‐genotyped subjects. Clinical Chemistry 2008;54(8):1356‐62. - PubMed
Merle 2009 {published data only}
-
- Merle U, Eisenbach C, Weiss KH. Serum ceruloplasmin oxidase activity is a sensitive and highly specific diagnostic marker for Wilson's disease. Journal of Hepatology 2009;51(5):925‐30. - PubMed
Nicastro 2010 {published data only}
-
- Nicastro E, Ranucci G, Vajro P, Vegnente A, Iorio R. Re‐evaluation of the diagnostic criteria for Wilson disease in children with mild liver disease. Hepatology 2010;52(6):1948‐56. - PubMed
Sezer 2014 {published data only}
-
- Sezer OB, Perk P, Hoşnut FÖ, Köse SK, Özcay F. Is it necessary to re‐evaluate diagnostic criteria for Wilson disease in children?. Turkish Journal of Gastroenterology 2014;25(6):690‐5. - PubMed
Xu 2018 {published data only}
References to studies excluded from this review
Causa 1997 {published data only}
-
- Cauza E, Maier‐Dobersberger T, Polli C, Kaserer K, Kramer L, Ferenci P. Screening for Wilson's disease in patients with liver diseases by serum ceruloplasmin. Journal of Hepatology 1997;27(2):358‐62. - PubMed
Frommer 1981 {published data only}
-
- Frommer DJ. Urinary copper excretion and hepatic copper concentrations in liver disease. Digestion 1981;21(4):169‐78. - PubMed
Gibbs 1979 {published data only}
-
- Gibbs K, Walshe JM. A study of the caeruloplasmin concentrations found in 75 patients with Wilson's disease, their kinships and various control groups. Quarterly Journal of Medicine 1979;48(191):477‐63. - PubMed
Gnanou 2006 {published data only}
-
- Gnanou JV, Thykadavil VG, Thuppil V. Pros and cons of immunochemical and enzymatic method in the diagnosis of Wilson's disease. Indian Journal of Medical Sciences 2006;60(9):371‐5. - PubMed
Lech 2007 {published data only}
-
- Lech T, Sadlik JK. Contribution to the data on copper concentration in blood and urine in patients with Wilson's disease and in normal subjects. Biological Trace Element Research 2007;118(1):16‐20. - PubMed
Li 1983 {published data only}
-
- Li NZ. The value of biochemical determination of copper in clinical diagnosis of hepatolenticular degeneration. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 1983;63(6):342‐5. - PubMed
Liggi 2013 {published data only}
-
- Liggi M, Mais C, Demurtas M, Sorbello O, Demelia E, Civolani A, et al. Uneven distribution of hepatic copper concentration and diagnostic value of double‐sample biopsy in Wilson's disease. Scandinavaian Journal of Gasteroenterology 2013;48(12):1452‐8. - PubMed
Mahjoub 2012 {published data only}
Markowitz 1955 {published data only}
-
- Markowitz H, Gubler CJ, Mahoney JP, Cartwright GE, Wintrobe MM. Studies on copper metabolism. XIV. Copper, ceruloplasmin and oxidase activity in sera of normal human subjects, pregnant women, and patients with infection, hepatolenticular degeneration and the nephrotic syndrome. Journal of Clinical Investigation 1955;34(10):1498‐508. - PMC - PubMed
Mzhel'skaia 1994 {published data only}
-
- Mzhel'skaia TI, Ivanova‐Smolenskaia IA, Korobova NV. Factors affecting the concentration of serum ceruloplasmin in Wilson‐Konovalov disease. Voprosy Meditsinskoi Khimii 1994;40(6):48‐53. - PubMed
Prasad 1998 {published data only}
-
- Prasad R, Kaur G, Walia BN. A critical evaluation of copper metabolism in Indian Wilson's disease children with special reference to their phenotypes and relatives. Biological Trace Element Research 1998;65(2):153‐65. - PubMed
Siotto 2014 {published data only}
-
- Siotto M, Pasqualetti P, Marano M, Squitti R. Automation of o‐dianisidine assay for ceruloplasmin activity analyses: usefulness of investigation in Wilson's disease and in hepatic encephalopathy. Journal of Neural Transmission (Vienna) 2014;121(10):1281‐6. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Aksu 2018 {published data only}
-
- Aksu AÜ, Sarı S, Gürkan ÖE, Dalgıç B. Urinary 24‐hour copper excretion at the time of diagnosis in children with Wilson's disease. Acta Gastro‐Enterologica Belgica 2018;81(3):410‐414. - PubMed
Zhou 2019 {published data only}
-
- Zhou XX, He RX, Pu XY, Li XH, Qin HL, Huang HW, Liang XL. Clinical characteristics of the Wilson disease carrier [肝豆状核变性携带者的临床特点及治疗策略]. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2019;99(11):806‐11. - PubMed
Additional references
Berman 1999
-
- Berman DH, Leventhal RI, Gavaler JS, Cadoff EM, Thiel DH. Clinical differentiation of fulminant wilsonian hepatitis from other causes of hepatic failure. Gastroenterology 1991;100(4):1129‐34. - PubMed
Bull 1993
-
- Bull PC, Thomas GR, Rommens JM, Forbes JR, Cox DW. The Wilson disease gene is a putative copper transporting P‐type ATPase similar to the Menkes gene. Nature Genetics 1993;5(4):327‐37. - PubMed
Coffey 2013
Compston 2009
-
- Compston A. Progressive lenticular degeneration: a familial nervous disease associated with cirrhosis of the liver, by S. A. Kinnier Wilson (From the National Hospital, and the Laboratory of the National Hospital, Queen Square, London) Brain 1912: 34; 295‐509. Brain 2009;132(Pt 8):295‐509. - PubMed
Cox 1966
-
- Cox DW. Factors influencing serum ceruloplasmin levels in normal individuals. Journal of Laboratory and Clinical Medicine 1966;68(6):893‐904. - PubMed
Czlonkowska 2009
-
- Czlonkowska A, Gromadzka G, Chabik G. Monozygotic female twins discordant for phenotype of Wilson’s disease. Movement Disorders 2009;24(7):1066‐9. - PubMed
Członkowska 2018
Davis 1996
-
- Davis W, Chowrimootoo GF, Seymour CA. Defective biliary copper excretion in Wilson's disease: the role of caeruloplasmin. European Journal of Clinical Investigation 1996;26(10):893‐901. - PubMed
Duncan 2016
-
- Duncan A, Yacoubian C, Beetham R, Catchpole A, Bullock D. The role of calculated non‐caeruloplasmin‐bound copper in Wilson's disease. Annals of Clinical Biochemistry 2016;54(6):649‐54. - PubMed
EASL 2012
-
- European Association for Study of Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Wilson's disease. Journal of Hepatology 2012;56(3):671‐85. - PubMed
El Balkhi 2011
-
- Balkhi S, Trocello JM, Poupon J, Chappuis P, Massicot F, Girardot‐Tinant N, et al. Relative exchangeable copper: a new highly sensitive and highly specific biomarker for Wilson's disease diagnosis. Clinica Chimica Acta 2011;412(23‐4):2254‐60. - PubMed
Ferenci 2003
-
- Ferenci P, Caca K, Loudianos G, Mieli‐Vergani G, Tanner S, Sternlieb I, et al. Diagnosis and phenotypic classification of Wilson disease. Liver International 2003;23(3):139‐42. - PubMed
Ferenci 2007
-
- Ferenci P, Członkowska A, Merle U, Ferenc S, Gromadzka G, Yurdaydin C. Late‐onset Wilson's disease. Gastroenterology 2007;132(4):1294‐8. - PubMed
Ferenci 2019
-
- Ferenci P, Stremmel W, Czlonkowska A, Szalay F, Viveiros A, Slattermayer AF, et al. Age and sex but not ATP7B genotype effectively influence the clinical phenotype of Wilson disease. Hepatology 2019;69(4):1464‐76. - PubMed
Giacchino 1997
-
- Giacchino R, Marazzi MG, Barabino A, Fasce L, Ciravegna B, Famularo L. Syndromic variability of Wilson's disease in children. Clinical study of 44 cases. Italian Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 1997;29(2):155‐61. - PubMed
Grazyna 2014
Gromadzka 2010
-
- Gromadzka G, Chabik G, Mendel T, Wierzchowska A, Rudnicka M, Czlonkowska A. Middle‐aged heterozygous carriers of Wilson's disease do not present with significant phenotypic deviations related to copper metabolism. Journal of Genetics 2010;89(4):463‐7. - PubMed
Hellman 2002
-
- Hellman NE, Gitlin JD. Ceruloplasmin metabolism and function. Annual Review of Nutrition 2002;22:439‐58. - PubMed
Huster 2012
Kelson 1978
-
- Kelson JR, Shamberger RJ. Methods compared for determining zinc in serum by flame atomic absorption spectroscopy. Clinical Chemistry 1978;24(2):240‐4. - PubMed
Kenney 2007
-
- Kenney SM, Cox DW. Sequence variation database for the Wilson disease copper transporter, ATP7B. Human Mutation 2007;28(12):1171‐7. - PubMed
Kingston 1986
-
- Kingston HM, Jassie LB. Microwave energy for acid decomposition at elevated temperatures and pressures using biological and botanical samples. Analytical Chemistry 1986;58(12):2534‐41. - PubMed
Korman 2008
LaRusso 1976
-
- LaRusso NF, Summerskill WH, McCall JT. Abnormalities of chemical tests for copper metabolism in chronic active liver disease: differentiation from Wilson's disease. Gasteroenterology 1976;70:653‐5. - PubMed
Lee 1998
Merle 2007
Ostapowicz 2002
-
- Ostapowicz G, Fontana RJ, Schiodt FV, Larson A, Davern TJ, Han SH, et al. Results of a prospective study of acute liver failure at 17 tertiary care centers in the United States. Annals of Internal Medicine 2002;137(12):947‐54. - PubMed
Perlman 1979
-
- Perman JA, Werlin SL, Grand RJ, Watkins JB. Laboratory measures of copper metabolism in the differentiation of chronic active hepatitis and Wilson disease in children. Journal of Pediatrics 1979;94(4):564‐8. - PubMed
Pfeiffenberger 2019
-
- Pfeiffenberger J, Lohse CM, Gotthardt D, Rupp C, Weiler M, Teufel U, et al. Long‐term evaluation of urinary copper excretion and non‐caeruloplasmin associated copper in Wilson disease patients under medical treatment. Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease 2019;42(2):371‐80. - PubMed
Poujois 2017
-
- Poujois A, Trocello JM, Djebrani‐Oussedik N, Poupon J, Collet C, Girardot‐Tinant N, et al. Exchangeable copper: a reflection of the neurological severity in Wilson's disease. European Journal of Neurology 2017;24(1):154‐60. - PubMed
PRISMA 2009
Roberts 2008
-
- Roberts EA, Schilsky ML. American Association for Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD). Diagnosis and treatment of Wilson disease: an update. Hepatology 2008;47(6):2089‐111. - PubMed
Rutter 2001
-
- Rutter CA, Gatsonis CA. A hierarchical regression approach to meta‐analysis of diagnostic test accuracy evaluations. Statistics in Medicine 2001;20(19):2865‐84. - PubMed
Sanchez‐Albisua 1999
-
- Sánchez‐Albisua I, Garde T, Hierro L, Camarena C, Frauca E, Vega A. A high index of suspicion: the key to an early diagnosis of Wilson's disease in childhood. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 1999;28(2):186‐90. - PubMed
Steindl 1997
-
- Steindl P, Ferenci P, Dienes HP, Grimm G, Pabinger I, Madl C, et al. Wilson's disease in patients presenting with liver disease: a diagnostic challenge. Gasteroenterology 1997;113(1):212‐8. - PubMed
Sternlieb 1990
-
- Sternlieb I. Perspectives on Wilson's disease. Hepatology 1990;12(5):1234‐39. - PubMed
Taly 2007
-
- Taly AB, Meenakshi‐Sundaram S, Sinha S, Swarmy HS, Arunodaya GR. Wilson disease: description of 282 patients evaluated over 3 decades. Medicine 2007;86(2):112‐21. - PubMed
Thomas 1995
-
- Thomas GR, Forbes JR, Roberts EA, Walshe JM, Cox DW. The Wilson disease gene: spectrum of mutations and their consequences. Nature Genetics 1995;9(2):210‐7. - PubMed
Tietz 2012a
-
- Hortin GL. Chapter 21 Amino acids, Peptides and Proteins. In: Burtis CA, Ashwood ER, Burns DE editor(s). Tietz Textbook of Clinical Chemistry and Molecular Diagnostics. 5th Edition. Elsevier, 2012:533‐5.
Tietz 2012b
-
- Kricka LJ, Park JY. Chapter 10 Optical Techniques. In: Burtis CA, Ashwood ER, Burns DE editor(s). Tietz Textbook of Clinical Chemistry and Molecular Diagnostics. 5th Edition. Elsevier, 2012:243‐4.
Tietz 2012c
-
- Shenkin A, Roberts NB. Chapter 31 Vitamins and Trace Elements. In: Burtis CA, Ashwood ER, Burns DE editor(s). Tietz Textbook of Clinical Chemistry and Molecular Diagnostics. 5th Edition. Elsevier, 2012:942‐3.
Twomey 2005
-
- Twomey PJ, Viljoen A, House IM, Reynolds TM, Wierzbicki AS. Relationship between serum copper, ceruloplasmin, and non‐ceruloplasmin‐bound copper in routine clinical practice. Clinical Chemistry 2005;;51(8):1558‐9. - PubMed
UK NEQAS 2018
-
- UK NEQAS for trace elements. External quality assurance scheme for trace elements. EQA SCHEME REPORT (accessed 06 October 2018).
Walshe 2003
-
- Walshe JM. Wilson’s disease: the importance of measuring serum caeruloplasmin non‐immunologically. Annals of Clinical Biochemistry 2003;40(Pt 2):115‐21. - PubMed
Walshe 2011
-
- Walshe JM. The eye in Wilson disease. QJM 2011;104(5):451‐3. - PubMed
Whiting 2011
-
- Whiting PF, Rutjes AWS, Westwood ME, Mallet S, Deeks JJ, Reitsma JB. QUADAS‐2: a revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Annals of Internal Medicine 2011;155(8):529‐36. - PubMed
Wilson 1987
-
- Willson RA, Clayson KJ, Leon S. Unmeasurable serum alkaline phosphatase activity in Wilson’s disease associated with fulminant hepatic failure and hemolysis. Hepatology 1987;7(3):613‐5. - PubMed
Zegers 2013
-
- Zegers I, Beetham R, Keller T, Sheldon J, Bullock D, MacKenzie F, et al. The importance of commutability of reference materials used as calibrators: the example of ceruloplasmin. Clinical Chemistry 2013;59(9):1322‐9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

