A Perspective on the Development of TGF-β Inhibitors for Cancer Treatment
- PMID: 31744193
- PMCID: PMC6921009
- DOI: 10.3390/biom9110743
A Perspective on the Development of TGF-β Inhibitors for Cancer Treatment
Abstract
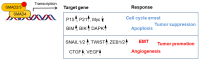
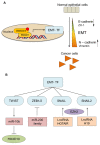
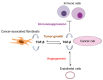
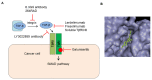
Transforming growth factor (TGF)-β is a secreted multifunctional cytokine that signals via plasma membrane TGF-β type I and type II receptors and intercellular SMAD transcriptional effectors. Aberrant inter- and intracellular TGF-β signaling can contribute to cancer progression. In normal cells and early stages of cancer, TGF-β can stimulate epithelial growth arrest and elicit a tumor suppressor function. However, in late stages of cancer, when the cytostatic effects of TGF-β in cancer cells are blocked, TGF-β signaling can act as tumor promoter by its ability to stimulate epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of cancer cells, by stimulating angiogenesis, and by promoting evasion of immune responses. In this review, we will discuss the rationale and challenges of targeting TGF-β signaling in cancer and summarize the clinical status of TGF-β signaling inhibitors that interfere with TGFβ bioavailability, TGF-βreceptor interaction, or TGF-β receptor kinase function. Moreover, we will discuss targeting of TGF-β signaling modulators and downstream effectors as well as alternative approaches by using promising technologies that may lead to entirely new classes of drugs.
Keywords: SMAD; TGF-β; cancer therapy; epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition; immune evasion; signaling; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

