Biological Effects of Anodic Oxidation on Titanium Miniscrews: An In Vitro Study on Human Cells
- PMID: 31744265
- PMCID: PMC6960790
- DOI: 10.3390/dj7040107
Biological Effects of Anodic Oxidation on Titanium Miniscrews: An In Vitro Study on Human Cells
Abstract
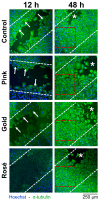
This controlled in vitro study compared the effects of varying the thickness of a TiO2 layer on cellular activity using commercially available miniscrew samples with identical surface features to derive information with direct clinical impact. Titanium grade V plates with four different thicknesses of TiO2 layer/color were used: absent/gray (Control group), 40-50 nm/pink (Pink group), 130 nm/gold (Gold group) and 140 nm/rosé (Rosé group). In vitro experiments used Saos-2 cells and included cell growth analysis, phospho-Histone H3 and procollagen I staining, cell viability analysis, and a cell migration assay at 12, 24, 40 and to 48 h. Few differences were seen among the groups, with no clear behavior of cellular activity according to the TiO2 thickness. The Control group showed a greater cell count. Phospho-Histone H3 staining was similar among the groups and procollagen I staining was greater in the Rosé group. Cell viability analysis showed a significant difference for live cell counts (greater in the Rosé group) and no difference for the dead cell counts. The cell migration assay showed a delay for the Rosé group up to 40 h, where full repopulation of cell-free areas was obtained at 48 h. The results suggest that the TiO2 layers of the commercial miniscrews have minimal biological effects, including cytotoxicity, with possibly negligible or minimal clinical implications.
Keywords: anodic oxidation; cell growth; miniscrews; orthodontics; titanium.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

