Outcome of primary rhegmatogenous retinal detachment using microincision vitrectomy and sutureless wide-angle viewing systems
- PMID: 31744475
- PMCID: PMC6862752
- DOI: 10.1186/s12886-019-1238-3
Outcome of primary rhegmatogenous retinal detachment using microincision vitrectomy and sutureless wide-angle viewing systems
Abstract
Background: To evaluate the efficacy of micro-incision vitrectomy surgery (MIVS) using Lumera and Resight non-contact sutureless wide-angle viewing systems (WAVS) for primary rhegmatogenous retinal detachment (RRD), and to analyze the anatomical and visual outcomes.
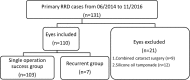
Methods: The retrospective, non-comparative, interventional case series reported here was conducted from June 2014 through November 2016. Enrolled patients presented with primary RRD and received MIVS with/without cryopexy by one surgeon using the Lumera and Resight non-contact sutureless WAVS. All patients were followed-up for a minimum of 12 months. Variables collected included patient demographics, best-corrected visual acuity, and macular status. The number and position of retinal break(s), and the use of cryopexy, were also recorded. Outcome measures included operative time, single-operation anatomical success rate, final anatomical success rate, recurrent rate, postoperative best-corrected visual acuity, and surgical complications. The end points were operative time, anatomical outcome, and functional outcome.
Results: In total, 110 eyes from 110 patients (68 men and 42 women) were treated. Of these, 103 (93%) eyes were reattached after primary vitrectomy. One hundred ten eyes (100%) reached final anatomical success. The mean operative time was 50.55 min. Multivariate analyses were performed with best model selection principle based on general linear model by Akaike Information Criteria for detecting possible factors related to operation time, and with multivariate logistic regression analysis for revealing probable clinical parameters which might influence the anatomical outcome after first operation and final visual outcome. Intraoperative cryopexy and multiple breaks increased operative time significantly. More favorable BCVA was significantly correlated with shorter operation time and the preoperative macula-on status. Multivariate logistic regression on the group of patients who have received the cataract surgery revealed that the pre-operative BCVA is a significant factor which can predict the visual outcome after MIVS.
Conclusions: The outcome of primary RRD repaired by MIVS using the Lumera and Resight sutureless WAVS was not inferior to any other published method. This instrument combination resulted in a relatively rapid and comfortable procedure without serious postoperative complications. Cryopexy and multiple breaks affected operative time significantly. Shorter operative times and preoperative macula-on status are associated with better final visual outcomes.
Keywords: Micro-incision vitrectomy surgery; Non-contact wide angle viewing system; Rhegmatogenous retinal detachment; Sutureless.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Repair of primary rhegmatogenous retinal detachment using 25-gauge transconjunctival sutureless vitrectomy.Retina. 2008 May;28(5):729-34. doi: 10.1097/IAE.0b013e318162b01c. Retina. 2008. PMID: 18463517
-
Outcomes and complications of rhegmatogenous retinal detachment repair with selective sutureless 25-gauge pars plana vitrectomy.Am J Ophthalmol. 2010 Apr;149(4):630-634.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2009.11.003. Epub 2010 Feb 6. Am J Ophthalmol. 2010. PMID: 20138604
-
Primary repair of retinal detachment with 25-gauge pars plana vitrectomy.Retina. 2008 Jul-Aug;28(7):931-6. doi: 10.1097/IAE.0b013e31816b313a. Retina. 2008. PMID: 18698293
-
Impact of the Time to Surgery on Visual Outcomes for Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment Repair: A Meta-Analysis.Am J Ophthalmol. 2022 Dec;244:19-29. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2022.07.022. Epub 2022 Aug 4. Am J Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35932819 Review.
-
Retinal Detachment Repair With Vitrectomy: Air Tamponade Integration to a Vitreoretinal Service, Comparison With Gas Tamponade, and Literature Review.Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging Retina. 2022 Feb;53(2):87-95. doi: 10.3928/23258160-20220121-02. Epub 2022 Feb 1. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging Retina. 2022. PMID: 35148215 Review.
Cited by
-
The contribution of the proximity of the retinal detachment to the fovea for postoperative metamorphopsia after 27-gauge pars plana vitrectomy for the primary rhegmatogenous retinal detachment.PLoS One. 2021 Oct 28;16(10):e0258775. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0258775. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34710146 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Vitrectomy without Using Perfluorocarbon Liquids and Drainage Retinotomy Associated with Postoperative Positioning Based on Residual Subretinal Fluid for Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment.J Ophthalmol. 2021 Apr 20;2021:5588479. doi: 10.1155/2021/5588479. eCollection 2021. J Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 33996150 Free PMC article.
-
Pigmentary lesions in eyes with rhegmatogenous retinal detachment with flap tears: a retrospective observational study.Sci Rep. 2022 Jul 21;12(1):12470. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-16508-5. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35864144 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical features of retinal detachment treated with segmental scleral buckling.Int Ophthalmol. 2024 Jul 2;44(1):304. doi: 10.1007/s10792-024-03186-7. Int Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 38954136 Free PMC article.
-
A Case of Intraocular Cilium after 25-Gauge Micro-Incision Vitrectomy Surgery.Case Rep Ophthalmol. 2023 Jan 3;14(1):1-6. doi: 10.1159/000528623. eCollection 2023 Jan-Dec. Case Rep Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 36654855 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmadieh H, Moradian S, Faghihi H, Parvaresh MM, Ghanbari H, Mehryar M, et al. Anatomic and visual outcomes of scleral buckling versus primary vitrectomy in pseudophakic and aphakic retinal detachment: six-month follow-up results of a single operation--report no. 1. Ophthalmology. 2005;112(8):1421–1429. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2005.02.018. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Machemer R, Buettner H, Norton EW, Parel JM. Vitrectomy: a pars plana approach. Trans Am Acad Ophthalmol Otolaryngol. 1971;75(4):813–820. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical