IL-17 receptor-based signaling and implications for disease
- PMID: 31745337
- PMCID: PMC6943935
- DOI: 10.1038/s41590-019-0514-y
IL-17 receptor-based signaling and implications for disease
Abstract
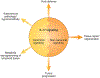
IL-17 is a highly versatile pro-inflammatory cytokine crucial for a variety of processes, including host defense, tissue repair, the pathogenesis of inflammatory disease and the progression of cancer. In contrast to its profound impact in vivo, IL-17 exhibits surprisingly moderate activity in cell-culture models, which presents a major knowledge gap about the molecular mechanisms of IL-17 signaling. Emerging studies are revealing a new dimension of complexity in the IL-17 pathway that may help explain its potent and diverse in vivo functions. Discoveries of new mRNA stabilizers and receptor-directed mRNA metabolism have provided insights into the means by which IL-17 cooperates functionally with other stimuli in driving inflammation, whether beneficial or destructive. The integration of IL-17 with growth-receptor signaling in specific cell types offers new understanding of the mitogenic effect of IL-17 on tissue repair and cancer. This Review summarizes new developments in IL-17 signaling and their pathophysiological implications.
Figures
References
-
- Rouvier E, Luciani MF, Mattei MG, Denizot F & Golstein P CTLA-8, cloned from an activated T cell, bearing AU-rich messenger RNA instability sequences, and homologous to a herpesvirus saimiri gene. J Immunol 150, 5445–5456 (1993). - PubMed
-
- Veldhoen M, Hocking RJ, Atkins CJ, Locksley RM & Stockinger B TGFbeta in the context of an inflammatory cytokine milieu supports de novo differentiation of IL-17-producing T cells. Immunity 24, 179–189 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Veldoen M Interleukin 17 is a chief orchestrator of immunity. Nat Immunol 18, 612–621 (2017). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

