VEGF signalling enhances lesion burden in KRIT1 deficient mice
- PMID: 31746130
- PMCID: PMC6933401
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.14773
VEGF signalling enhances lesion burden in KRIT1 deficient mice
Abstract
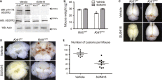
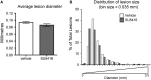
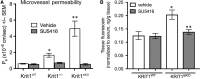
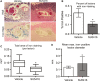
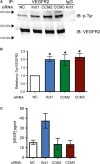
The exact molecular mechanisms underlying CCM pathogenesis remain a complicated and controversial topic. Our previous work illustrated an important VEGF signalling loop in KRIT1 depleted endothelial cells. As VEGF is a major mediator of many vascular pathologies, we asked whether the increased VEGF signalling downstream of KRIT1 depletion was involved in CCM formation. Using an inducible KRIT1 endothelial-specific knockout mouse that models CCM, we show that VEGFR2 activation plays a role in CCM pathogenesis in mice. Inhibition of VEGFR2 using a specific inhibitor, SU5416, significantly decreased the number of lesions formed and slightly lowered the average lesion size. Notably, VEGFR2 inhibition also decreased the appearance of lesion haemorrhage as denoted by the presence of free iron in adjacent tissues. The presence of free iron correlated with increased microvessel permeability in both skeletal muscle and brain, which was completely reversed by SU5416 treatment. Finally, we show that VEGFR2 activation is a common downstream consequence of KRIT1, CCM2 and CCM3 loss of function, though the mechanism by which VEGFR2 activation occurs likely varies. Thus, our study clearly shows that VEGFR2 activation downstream of KRIT1 depletion enhances the severity of CCM formation in mice, and suggests that targeting VEGF signalling may be a potential future therapy for CCM.
Keywords: angiogenesis; cerebral cavernous malformation; haemorrhagic stroke; vascular endothelial growth factor.
© 2019 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
KRIT1 protein depletion modifies endothelial cell behavior via increased vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling.J Biol Chem. 2014 Nov 21;289(47):33054-65. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.582304. Epub 2014 Oct 15. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25320085 Free PMC article.
-
Production of KRIT1-knockout and KRIT1-knockin Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts as Cellular Models of CCM Disease.Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2152:151-167. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-0640-7_12. Methods Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 32524551
-
Cerebral cavernous malformations proteins inhibit Rho kinase to stabilize vascular integrity.J Exp Med. 2010 Apr 12;207(4):881-96. doi: 10.1084/jem.20091258. Epub 2010 Mar 22. J Exp Med. 2010. PMID: 20308363 Free PMC article.
-
KRIT1 in vascular biology and beyond.Biosci Rep. 2024 Jul 31;44(7):BSR20231675. doi: 10.1042/BSR20231675. Biosci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38980708 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KRIT1: A Traffic Warden at the Busy Crossroads Between Redox Signaling and the Pathogenesis of Cerebral Cavernous Malformation Disease.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2023 Mar;38(7-9):496-528. doi: 10.1089/ars.2021.0263. Epub 2022 Nov 1. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2023. PMID: 36047808 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Persistent Activation of Endothelial Cells is Linked to Thrombosis and Inflammation in Cerebral Cavernous Malformation Disease.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jul 2:2025.06.29.662238. doi: 10.1101/2025.06.29.662238. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40631268 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Mild Hypoxia Accelerates Cerebral Cavernous Malformation Disease Through CX3CR1-CX3CL1 Signaling.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2024 Jun;44(6):1246-1264. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.123.320367. Epub 2024 Apr 25. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2024. PMID: 38660801 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of protein-protein interactions to the endothelial-barrier-stabilizing function of KRIT1.J Cell Sci. 2022 Jan 15;135(2):jcs258816. doi: 10.1242/jcs.258816. Epub 2022 Jan 25. J Cell Sci. 2022. PMID: 34918736 Free PMC article.
-
Is Location Everything? Regulation of the Endothelial CCM Signaling Complex.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Jul 11;9:954780. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.954780. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35898265 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanism of the HIF-1α/VEGF/VEGFR-2 pathway in the proliferation and apoptosis of human haemangioma endothelial cells.Int J Exp Pathol. 2023 Oct;104(5):258-268. doi: 10.1111/iep.12485. Epub 2023 Jun 28. Int J Exp Pathol. 2023. PMID: 37381118 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Labauge P, Brunereau L, Levy C, Laberge S, Houtteville JP. The natural history of familial cerebral cavernomas: a retrospective MRI study of 40 patients. Neuroradiology. 2000;42(5):327‐332. - PubMed
-
- Krisht KM, Whitehead KJ, Niazi T, Couldwell WT. The pathogenetic features of cerebral cavernous malformations: a comprehensive review with therapeutic implications. Neurosurg Focus. 2010;29(3):E2. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

