Exploratory study on application of MALDI‑TOF‑MS to detect serum and urine peptides related to small cell lung carcinoma
- PMID: 31746355
- PMCID: PMC6896340
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10794
Exploratory study on application of MALDI‑TOF‑MS to detect serum and urine peptides related to small cell lung carcinoma
Abstract
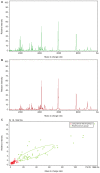
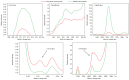
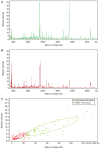
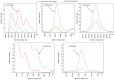
Matrix‑assisted laser desorption/ionization time‑of‑flight mass spectrometry (MALDI‑TOF‑MS) was employed to analyze differential serum and urine peptides in patients with small cell lung cancer (SCLC) and healthy individuals, and SCLC diagnostic classification models were constructed. Serum and urine samples from 72 patients with SCLC, age‑ and gender‑matched with 72 healthy individuals, were divided into training and testing sets in a 3:1 ratio. Serum and urine peptides were extracted using copper ion‑chelating nanomagnetic beads, and mass spectra were obtained using MALDI‑TOF‑MS. Peptide spectra for the training set were analyzed, and the classification model was constructed using ClinProTools (CPT). The testing set was used for blinded model validation. For training‑set sera, 122 differential peptide signal peaks with a mass of 0.8‑10 kDa were observed, and 19 peptides showed significantly different expression [P<0.0005; area under curve (AUC) ≥0.80]. CPT screened 5 peptide peaks (0.8114, 0.83425, 1.86655, 4.11133 and 5.81192 kDa) to construct the classification model. The testing set was used for the blinded validation, which had 95.0% sensitivity and 90.0% specificity. For the training‑set urine, 132 differential peptide signal peaks with m/z ratios of 0.8‑10 kDa were observed, and 8 peptides had significantly different expression (P<0.0005; AUC ≥0.80). Then, 5 peaks (1.0724, 2.37692, 2.7554, 4.75475 and 4.7949 kDa) were used for classification model construction. The testing set was used for 36 blinded validation, which had 85.0% sensitivity and 80.0% specificity. Among the differential peptides, 3 had the same significant peaks at 2.3764, 0.8778 and 0.8616 kDa, identified as fibrinogen α, glucose‑6‑phosphate isomerase and cyclin‑dependent kinase‑1, respectively. The present study highlighted the differences that exist in serum and urine peptides between patients with SCLC and healthy individuals. Serum and urine peptide diagnostic classification models could be constructed using MALDI‑TOF‑MS, and showed high sensitivity and specificity.
Keywords: Maldi-ToF-MS; proteomics; serum; small cell lung carcinoma; urine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Preliminary study of MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry-based screening of patients with the NSCLC serum-specific peptides].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2013 May;16(5):233-9. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2013.05.04. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 23676979 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
[Detection of Serum Peptides in Patients with Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma by MALDI-TOF-MS and Analysis of Their Correlation with Chemotherapy Efficacy].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2017 May 20;20(5):318-325. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2017.05.04. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 28532539 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Serum peptidome profiling in patients with lung cancer.Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2010 Dec;293(12):2027-33. doi: 10.1002/ar.21267. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2010. PMID: 21082738
-
[Identification of serum peptide biomarker for ovarian cancer diagnosis by Clin-TOF-II-MS combined with magnetic beads technology].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2021 Nov 23;43(11):1188-1195. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112152-20210315-00229. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34794222 Chinese.
-
Classification of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Gene Mutation Status Using Serum Proteomic Profiling Predicts Tumor Response in Patients with Stage IIIB or IV Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 5;10(6):e0128970. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128970. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26047516 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Targeted O-glycoproteomics for the development of diagnostic markers for advanced colorectal cancer.Front Oncol. 2023 Feb 9;13:1104936. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1104936. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36845686 Free PMC article.
-
Advancements in Oncoproteomics Technologies: Treading toward Translation into Clinical Practice.Proteomes. 2023 Jan 10;11(1):2. doi: 10.3390/proteomes11010002. Proteomes. 2023. PMID: 36648960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomic Profiling of Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Oct 16;15(20):5005. doi: 10.3390/cancers15205005. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37894372 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MALDI-TOF-MS analysis in low molecular weight serum peptidome biomarkers for NSCLC.J Clin Lab Anal. 2022 Apr;36(4):e24254. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24254. Epub 2022 Feb 25. J Clin Lab Anal. 2022. PMID: 35212031 Free PMC article.
-
MALDI-TOF/MS Analysis of Non-Invasive Human Urine and Saliva Samples for the Identification of New Cancer Biomarkers.Molecules. 2022 Mar 16;27(6):1925. doi: 10.3390/molecules27061925. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35335287 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Ervik M, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D, Bray F. 11 [Internet] International Agency for Research on Cancer; Lyon: 2014. GLOBOCAN 2012 v1.0, Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: IARC cancer base no.
-
- National Central Cancer Registry of China, corp-author. China Cancer Registration Annual Report. 2014
-
- Evans WK, Flanagan WM, Miller AB, Goffin JR, Memon S, Fitzgerald N, Wolfson MC. Implementing low-dose computed tomography screening for lung cancer in Canada: Implications of alternative at-risk populations, screening frequency, and duration. Curr Oncol. 2016;23:e179–e187. doi: 10.3747/co.23.2988. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

