Roxatidine inhibits fibrosis by inhibiting NF‑κB and MAPK signaling in macrophages sensing breast implant surface materials
- PMID: 31746427
- PMCID: PMC6896367
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10815
Roxatidine inhibits fibrosis by inhibiting NF‑κB and MAPK signaling in macrophages sensing breast implant surface materials
Abstract
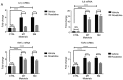
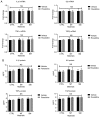
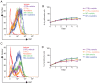
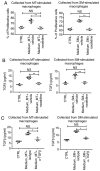
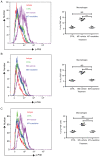
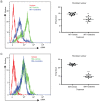
Capsular contracture is an important complication after silicone mammary implant surgery. Fibroblasts and macrophages play critical roles in the pathogenesis of capsular contracture, making these two cell types therapeutic targets. It has been reported that inhibiting histamine receptors results attenuates fibrosis, but the role of roxatidine (a histamine receptor 2 inhibitor) in preventing fibrosis caused by breast implant materials remains unknown. The aim of the present study was to assess the hypothesis that roxatidine might have a prophylactic effect in capsular contracture induced by implant material. Inflammation induced by breast implant materials was mimicked by co‑culturing macrophages or fibroblasts with these materials in vitro. Capsular contracture was modeled in mice by planting breast implant materials in a subcutaneous pocket. Roxatidine was added in the culture medium or administered to mice bearing breast implant materials. By co‑culturing macrophages or fibroblasts with common breast implant materials (micro‑textured or smooth breast implants), the present study demonstrated that macrophages respond to these materials by producing pro‑inflammatory cytokines, a process that was abolished by addition of roxatidine to the culture medium. Although fibroblasts did not respond to implant surface materials in the same way as macrophages, the conditioned media of macrophages induced proliferation of fibroblasts. Mechanistically, administration of roxatidine inhibited activation of NF‑κB and p38/mitogen‑activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling in macrophages. Furthermore, treatment with roxatidine in implant‑bearing mice reduced serum concentrations of transforming growth factor‑β and the abundance of fibroblasts around the implant. The present study concluded that roxatidine plays an important role in preventing fibrosis by inhibiting activation of NF‑κB and p38/MAPK signaling in macrophages.
Keywords: mammary implant; capsular contracture; macrophage; fibroblast; roxatidine.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Roxatidine suppresses inflammatory responses via inhibition of NF-κB and p38 MAPK activation in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages.J Cell Biochem. 2011 Dec;112(12):3648-59. doi: 10.1002/jcb.23294. J Cell Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21809375
-
Delaying implant-based mammary reconstruction after radiotherapy does not decrease capsular contracture: An in vitro study.J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2017 Sep;70(9):1210-1217. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2017.06.012. Epub 2017 Jun 17. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2017. PMID: 28687257
-
Serologic and histologic findings in patients with capsular contracture after breast augmentation with smooth silicone gel implants: is serum hyaluronan a potential predictor?Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2005 Nov-Dec;29(6):510-8. doi: 10.1007/s00266-005-5049-y. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2005. PMID: 16328636
-
Comparison of the postoperative incidence rate of capsular contracture among different breast implants: a cumulative meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2015 Feb 13;10(2):e0116071. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116071. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25680100 Free PMC article.
-
Non-surgical Treatment and Prophylaxis of Capsular Contracture in Mammary Implants: A Systematic Review of Literature.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2025 Apr 21. doi: 10.1007/s00266-025-04879-9. Online ahead of print. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2025. PMID: 40259064 Review.
Cited by
-
Mycobacterium tuberculosis Utilizes Host Histamine Receptor H1 to Modulate Reactive Oxygen Species Production and Phagosome Maturation via the p38MAPK-NOX2 Axis.mBio. 2022 Oct 26;13(5):e0200422. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02004-22. Epub 2022 Aug 24. mBio. 2022. PMID: 36000734 Free PMC article.
-
Is It All about Surface Topography? An Intra-Individual Clinical Outcome Analysis of Two Different Implant Surfaces in Breast Reconstruction.J Clin Med. 2023 Feb 7;12(4):1315. doi: 10.3390/jcm12041315. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36835850 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative randomized trial evaluating the effect of proton pump inhibitor versus histamine 2 receptor antagonist as an adjuvant therapy in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Med Oncol. 2021 Jan 4;38(1):4. doi: 10.1007/s12032-020-01452-z. Med Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33394214 Clinical Trial.
-
Capsular Contracture in Breast Implant Surgery: Where Are We Now and Where Are We Going?Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2021 Jun;45(3):1328-1337. doi: 10.1007/s00266-021-02141-6. Epub 2021 Feb 8. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2021. PMID: 33559094
-
Quantitative Proteomic Characterization of Foreign Body Response towards Silicone Breast Implants Identifies Chronological Disease-Relevant Biomarker Dynamics.Biomolecules. 2023 Feb 6;13(2):305. doi: 10.3390/biom13020305. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 36830674 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Johnson M. Breast implants: History, safety, and imaging. Radiol Technol. 2013;84:439M–520M. - PubMed
-
- Cappellano G, Ploner C, Lobenwein S, Sopper S, Hoertnagl P, Mayerl C, Wick N, Pierer G, Wick G, Wolfram D. Immunophenotypic characterization of human T cells after in vitro exposure to different silicone breast implant surfaces. PLoS One. 2018;13:e0192108. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0192108. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

