Gas-Phase Sequencing of Cyclotides: Introduction of Selective Ring Opening at Dehydroalanine via Ion/Ion Reaction
- PMID: 31746593
- PMCID: PMC6917824
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.9b03671
Gas-Phase Sequencing of Cyclotides: Introduction of Selective Ring Opening at Dehydroalanine via Ion/Ion Reaction
Abstract
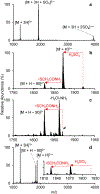
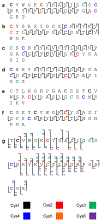
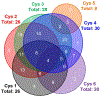
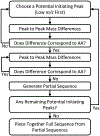
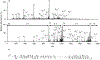
The gas-phase linearization of cyclotides via site-selective ring opening at dehydroalanine residues and its application to cyclotide sequencing is presented. This strategy relies on the ability to incorporate dehydroalanine into macrocyclic peptide ions, which is easily accomplished through an ion/ion reaction. Triply protonated cyclotide cations are transformed into radical cations via ion/ion reaction with the sulfate radical anion. Subsequent activation of the cyclotide radical cation generates dehydroalanine at a single cysteine residue, which is easily identified by the odd-electron loss of ·SCH2CONH2. The presence of dehydroalanine in cyclotides provides a site-selective ring-opening pathway that, in turn, generates linear cyclotide analogues in the gas phase. Unlike cyclic variants, product ions derived from the linear peptides provide rich sequence information. The sequencing capability of this strategy is demonstrated with four known cyclotides found in Viola inconspicua, where, in each case, greater than 93% sequence coverage was observed. Furthermore, the utility of this method is highlighted by the partial de novo sequencing of an unknown cyclotide with much greater sequence coverage than that obtained with a conventional Glu-C digestion approach. This method is particularly well-suited for cyclotide species that are not abundant enough to characterize with traditional methods.
Figures


References
-
- Craik DJ, Daly NL, Bond T, Waine C: Plant cyclotides: A unique family of cyclic and knotted proteins that defines the cyclic cystine knot structural motif. J. Mol. Biol 294, 1327–1336 (1999) - PubMed
-
- Colgrave ML, Craik DJ: Thermal, Chemical, and Enzymatic Stability of the Cyclotide Kalata B1: The Importance of the Cyclic Cystine Knot. Biochemistry. 43, 5965–5975 (2004) - PubMed
-
- Henriques ST, Craik DJ: Cyclotides as templates in drug design. Drug Discov. Today 15, 57–64 (2010) - PubMed
-
- Poth AG, Chan LY, Craik DJ: Cyclotides as grafting frameworks for protein engineering and drug design applications. J. Pept. Sci 100, 480–491 (2013) - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

