Blockade of angiotensin-converting enzyme or tumor necrosis factor-α reverses maternal high-fat diet-induced sensitization of angiotensin II hypertension in male rat offspring
- PMID: 31746626
- PMCID: PMC7052597
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.00200.2019
Blockade of angiotensin-converting enzyme or tumor necrosis factor-α reverses maternal high-fat diet-induced sensitization of angiotensin II hypertension in male rat offspring
Abstract
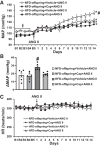
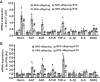
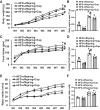
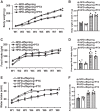
Maternal high-fat diet (HFD) is associated with metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular diseases in adult offspring. Our previous study demonstrated that maternal HFD enhances pressor responses to ANG II or a proinflammatory cytokine (PIC), which is associated with increased expression of brain renin-angiotensin system (RAS) components and PICs in adult offspring. The present study further investigated whether inhibition of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) or tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) blocks sensitization of ANG II hypertension in offspring of HFD dams. All offspring were bred from dams with normal fat diet (NFD) or HFD starting two weeks before mating and maintained until weaning of the offspring. Then the weaned offspring were treated with an ACE inhibitor (captopril) or a TNF-α inhibitor (pentoxifylline) in the drinking water through the end of testing with a slow-pressor dose of ANG II. RT-PCR analyses of the lamina terminalis and paraventricular nucleus revealed upregulation of mRNA expression of several RAS components and PICs in male offspring of HFD dams when compared with age-matched offspring of NFD dams. The enhanced gene expression was attenuated by blockade of either RAS or PICs. Likewise, ANG II administration produced an augmented pressor response in offspring of HFD dams. This was abolished by either ACE or TNF-α inhibitor. Taken together, this study provides mechanistic evidence and a therapeutic strategy that systemic inhibition of the RAS and PICs can block maternal HFD-induced sensitization of ANG II hypertension, which is associated with attenuation of brain RAS and PIC expression in offspring.
Keywords: blood pressure; inflammation; maternal high-fat diet; renin-angiotensin system.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Maternal high-fat diet acts on the brain to induce baroreflex dysfunction and sensitization of angiotensin II-induced hypertension in adult offspring.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018 May 1;314(5):H1061-H1069. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00698.2017. Epub 2018 Jan 26. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29373045 Free PMC article.
-
Stress-Induced Sensitization of Angiotensin II Hypertension Is Reversed by Blockade of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme or Tumor Necrosis Factor-α.Am J Hypertens. 2019 Aug 14;32(9):909-917. doi: 10.1093/ajh/hpz075. Am J Hypertens. 2019. PMID: 31063551 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal Gestational Hypertension-Induced Sensitization of Angiotensin II Hypertension Is Reversed by Renal Denervation or Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibition in Rat Offspring.Hypertension. 2017 Apr;69(4):669-677. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.116.08597. Epub 2017 Feb 21. Hypertension. 2017. PMID: 28223469 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of renin-angiotensin system inhibition on end-organ protection: can we do better?Clin Ther. 2007 Sep;29(9):1803-24. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2007.09.019. Clin Ther. 2007. PMID: 18035185 Review.
-
Recent changes in the landscape of combination RAS blockade.Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2009 Nov;7(11):1373-84. doi: 10.1586/erc.09.127. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2009. PMID: 19900020 Review.
Cited by
-
Protection by -Biotics against Hypertension Programmed by Maternal High Fructose Diet: Rectification of Dysregulated Expression of Short-Chain Fatty Acid Receptors in the Hypothalamic Paraventricular Nucleus of Adult Offspring.Nutrients. 2022 Oct 14;14(20):4306. doi: 10.3390/nu14204306. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36296991 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal Angiotensin II-Induced Hypertension Sensitizes Postweaning High-Fat Diet-Elicited Hypertensive Response Through Increased Brain Reactivity in Rat Offspring.J Am Heart Assoc. 2021 Sep 21;10(18):e022170. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.121.022170. Epub 2021 Sep 6. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021. PMID: 34482712 Free PMC article.
-
Appraising the Preclinical Evidence of the Role of the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System in Antenatal Programming of Maternal and Offspring Cardiovascular Health Across the Life Course: Moving the Field Forward: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association.Hypertension. 2023 May;80(5):e75-e89. doi: 10.1161/HYP.0000000000000227. Epub 2023 Mar 23. Hypertension. 2023. PMID: 36951054 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interactions of the Brain Renin-Angiotensin-System (RAS) and Inflammation in the Sensitization of Hypertension.Front Neurosci. 2020 Jul 15;14:650. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00650. eCollection 2020. Front Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32760236 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Involvement of the Renin-Angiotensin System in Stress: State of the Art and Research Perspectives.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2022;20(6):1212-1228. doi: 10.2174/1570159X19666210719142300. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34554902 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

