Co-targeting p53-R249S and CDK4 synergistically suppresses survival of hepatocellular carcinoma cells
- PMID: 31747859
- PMCID: PMC7012101
- DOI: 10.1080/15384047.2019.1685289
Co-targeting p53-R249S and CDK4 synergistically suppresses survival of hepatocellular carcinoma cells
Abstract
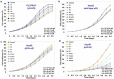
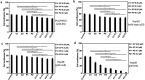
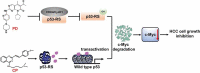
p53-R249S (p53-RS) is frequently detected in human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) that is highly associated with hepatitis B infection and aflatoxin B1 exposure. Our previous study showed that CDK4/Cyclin D1 phosphorylates p53-RS at the cancer-derived Ser249 and promotes its interaction with c-Myc in the nucleus, consequently enhancing c-Myc-dependent ribosomal biogenesis and HCC cell proliferation. Here we explored the possibility of co-targeting CDK4 and p53-RS with available small molecule inhibitors as a potential combined therapy for HCC that harbor p53-RS. Indeed, co-treatment of p53-RS-containing, but not wild-type p53 or p53-null, HCC cells with PD-0332991 (PD), a CDK4/6 inhibitor, and CP-31398 (CP), a compound that can restore the intrinsic conformation and transcriptional activity of mutant p53, drastically repressed the c-Myc activation function of p53-RS. This combination of PD with CP exhibited a synergistic effect on the inhibition of HCC cell growth in a p53-RS dependent manner, especially at a lower dose. These results suggest that co-targeting CDK4 and p53-RS can serve as a potential approach for the development of an effective therapy for HCC that harbor p53-RS.
Keywords: CDK4/Cyclin D1; CP-31398; HCC; PD-0332991; Synergistic effect; c-Myc; p53-R249S.
Figures




References
-
- Aghemo A, Colombo M.. Hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis C: from bench to bedside. Semin Immunopathol. 2013;35:111–120. - PubMed
-
- Sangiovanni A, Del Ninno E, Fasani P, De Fazio C, Ronchi G, Romeo R, Morabito A, De Franchis R, Colombo M.. Increased survival of cirrhotic patients with a hepatocellular carcinoma detected during surveillance. Gastroenterol. 2004;126:1005–1014. - PubMed
-
- Cheng P, Cheng Y, Su MX, Li D, Zhao GZ, Gao H, Li Y, Zhu JY, Li H, Zhang T. Bicluster and pathway enrichment analysis of HCV-induced cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Asian Pac J Canc Prev. 2012;13:3741–3745. - PubMed
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
