Harmonic Scalpel Versus Coblation Tonsillectomy A Comparative Study
- PMID: 31750110
- PMCID: PMC6838272
- DOI: 10.1007/s12070-019-01679-x
Harmonic Scalpel Versus Coblation Tonsillectomy A Comparative Study
Abstract
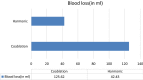
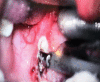
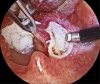
Tonsillectomy is an age old procedure in ENT practice. Though traditional dissection method is gold standard, we surgeons are trying different techniques like electrocautery, coblation, harmonic scalpel (HS) mainly to improve surgical convenience, to decrease operative time, post operative pain, intra and post operative bleeding and fast return to normal life. In this particular study we are comparing coblation and HS as surgical tool in tonsillectomy. It is a prospective double-blind randomized controlled trial where information was compared between two groups of coblation and HS tonsillectomy. A total number of 128 patients were compared over operation time, intra-operative blood loss, postoperative pain, time needed to regain the normal diet and activity and postoperative haemorrhage. We found statistically significant differences in operation time (p < 0.001) and intra operative blood loss (p < 0.001). Secondary haemorrhage rate was far better in HS (1.5%) group compared to coblation (7.8%). Whereas postoperative pain, time needed to go back to the normal diet and activity were better in HS group but the difference is not significant. This study revealed a significantly less operative time and intra-operative and post operative blood loss in harmonic scalpel tonsillectomy in comparison with coblation method. These findings addressed HS tonsillectomy as an advanced method.
Keywords: Coblation; Harmonic; Tonsillectomy.
© Association of Otolaryngologists of India 2019.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous