Magnitude and factors associated with anemia among pregnant women attending antenatal care in Bench Maji, Keffa and Sheka zones of public hospitals, Southwest, Ethiopia, 2018: A cross -sectional study
- PMID: 31751368
- PMCID: PMC6872185
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0225148
Magnitude and factors associated with anemia among pregnant women attending antenatal care in Bench Maji, Keffa and Sheka zones of public hospitals, Southwest, Ethiopia, 2018: A cross -sectional study
Abstract
Background: Anemia during pregnancy is a common public health problem globally and it defined as the hemoglobin concentration of less than 11 g/dl. Anemia during pregnancy has maternal and perinatal diverse consequences and it increase the risk of maternal and perinatal mortality. The aim of this study is to assess magnitude and factors associated with anemia among pregnant women attending antenatal care in Bench Maji, Keffa and Sheka zones of public hospitals, South west, Ethiopia, 2018.
Methods: A cross-sectional study was employed on 1871 pregnant mothers from selected hospitals. All third trimester pregnant women attending antenatal care at Mizan-Tepi University Teaching Hospital, Tepi, Gebretsadik Shawo and Wacha public hospitals were included in the study. Data was entered to Epidata version 3.1 and exported to SPSS version 21 for analysis. Logistic regression analysis was carried out to identify independently associate factors at confidence interval of 95% and significance level of P-value <0.05.
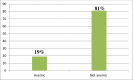
Result: The magnitude of anemia in this study from the total study participant was 356 (19.0%). Among anemic pregnant women, 330 (92.7%), 21(5.9%) and 5(1.4%) were mild anemia, moderate anemia and severe anemia respectively. Age group 20-24 [AOR 6.28(2.40-16.42)], 25-29 [AOR = 6.38 (2.71-15.01)], 30-34 [AOR = 5.13 (2.27-11.58) and age ≥35 years [AOR = 2.53 (1.07-5.98)], educational status (read and write) [AOR 2.06, 95% CI (1.12-3.80)], gestational age(term)[AOR 1.94, 95% CI (1.27-2.96)], Caffeine (coffee and tea) and alcohol use occasionally [AOR 2.01, 95% CI (1.14-3.55)] and [AOR 2.59, 95% CI (1.49-4.52)] respectively, nutritional status (under nutrition) [AOR 3.00, 95% CI (2.22-3.97)] and family size (>6) [AOR 2.66, 95% CI (1.49-4.77)] were factors associated with anemia.
Conclusion: The magnitude of anemia found to be high. Age, educational status of the mother, gestational age, caffeine and alcohol use, Nutritional status and family size were factors significantly associated with anemia. To prevent adverse outcome of anemia, health care providers should work on these factors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nutritional factors for anemia in pregnancy: A systematic review with meta-analysis.Front Public Health. 2022 Oct 14;10:1041136. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1041136. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36311562 Free PMC article.
-
Magnitude and factors associated with anemia among pregnant women attending antenatal care in public health centers in central zone of Tigray region, northern Ethiopia: a cross sectional study.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2018 Nov 1;18(1):433. doi: 10.1186/s12884-018-2063-z. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2018. PMID: 30382868 Free PMC article.
-
Anemia and Associated Factors Among Pregnant Women Attending Antenatal Care Clinic in Wolayita Sodo Town, Southern Ethiopia.Ethiop J Health Sci. 2015 Apr;25(2):155-62. doi: 10.4314/ejhs.v25i2.8. Ethiop J Health Sci. 2015. PMID: 26124623 Free PMC article.
-
Magnitude of anemia and associated factors among pregnant women attending antenatal care in governmental health facilities of Shashemene Town, Oromia region, Ethiopia.Front Public Health. 2024 Sep 4;12:1409752. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1409752. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39296845 Free PMC article.
-
Date palm (Phoenix dactylifera) consumption as a nutrition source for mild anemia.Gac Sanit. 2021;35 Suppl 2:S271-S274. doi: 10.1016/j.gaceta.2021.10.032. Gac Sanit. 2021. PMID: 34929829 Review.
Cited by
-
Predicting the level of anemia among Ethiopian pregnant women using homogeneous ensemble machine learning algorithm.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2022 Sep 22;22(1):247. doi: 10.1186/s12911-022-01992-6. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2022. PMID: 36138398 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary iron intakes and odds of iron deficiency anaemia among pregnant women in Ifako-Ijaiye, Lagos, Nigeria: a cross-sectional study.Pan Afr Med J. 2022 May 11;42:23. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2022.42.23.29965. eCollection 2022. Pan Afr Med J. 2022. PMID: 35910059 Free PMC article.
-
Nutritional factors for anemia in pregnancy: A systematic review with meta-analysis.Front Public Health. 2022 Oct 14;10:1041136. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1041136. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36311562 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and predictors of anemia among pregnant women in Ethiopia: Systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2022 Jul 27;17(7):e0267005. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0267005. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35895619 Free PMC article.
-
Magnitude of Anemia and Its Associated Factors Among Pregnant Women Attending Antenatal Care in Hiwot Fana Specialized University Hospital in Eastern Ethiopia.Front Public Health. 2022 May 30;10:867888. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.867888. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35719616 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Organization WH. The global prevalence of anaemia in 2011. The global prevalence of anaemia in 20112015.
-
- Balarajan Y, Ramakrishnan U, Özaltin E, Shankar AH, Subramanian S. Anaemia in low-income and middle-income countries. The lancet. 2011;378 (9809):2123–35. - PubMed
-
- Paola Aghajanian, Steven W, Mohammed W, Ellene Andrew, Dennis R, et al. (2007). Current Diagnosis and Treatment Obstetrics & Gynecology, Tenth Edition, McGraw-Hill Companies.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical