Olfactory Learning in the Stingless Bee Melipona eburnea Friese (Apidae: Meliponini)
- PMID: 31752087
- PMCID: PMC6920981
- DOI: 10.3390/insects10110412
Olfactory Learning in the Stingless Bee Melipona eburnea Friese (Apidae: Meliponini)
Abstract
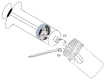
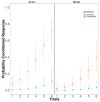
Olfactory learning and floral scents are co-adaptive traits in the plant-pollinator relationship. However, how scent relates to cognition and learning in the diverse group of Neotropical stingless bees is largely unknown. Here we evaluated the ability of Melipona eburnea to be conditioned to scent using the proboscis extension reflex (PER) protocol. Stingless bees did not show PER while harnessed but were able to be PER conditioned to scent when free-to-move in a mini-cage (fmPER). We evaluated the effect of: 1) unconditioned stimulus (US) reward, and 2) previous scent-reward associations on olfactory learning performance. When using unscented-US, PER-responses were low on day 1, but using scented-US reward the olfactory PER-response increased on day 1. On day 2 PER performance greatly increased in bees that previously had experienced the same odor and reward combination, while bees that experienced a different odor on day 2 showed poor olfactory learning. Bees showed higher olfactory PER conditioning to guava than to mango odor. The effect of the unconditioned stimulus reward was not a significant factor in the model on day 2. This indicates that olfactory learning performance can increase via either taste receptors or accumulated experience with the same odor. Our results have application in agriculture and pollination ecology.
Keywords: Free-moving-PER (fmPER); conditioning protocols; learning; olfactory conditioning, cognitive ecology; pollinators; scented-US; stingless-bees.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Abramson C.I. Invertebrate Learning: A Laboratory Manual and Source Book. American Psychological Association; Washington, DC, USA: 1990. pp. 22–54.
-
- Abramson C.I. A Primer of Invertebrate Learning: The Behavioral Perspective. American Psychological Association; Washington, DC, USA: 1994. [(accessed on 12 August 2019)]. Available online: https://books.google.com.co/books?id=0D9mQgAACAAJ.
-
- Dukas R. Evolutionary Biology of Animal Cognition. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2004;35:347–374. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.35.112202.130152. - DOI
-
- Real L.A. Information Processing and the Evolutionary Ecology of Cognitive Architecture. Am. Nat. 1992;140:S108–S145. doi: 10.1086/285399. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

