Enhancement of zaleplon oral bioavailability using optimized self-nano emulsifying drug delivery systems and its effect on sleep quality among a sample of psychiatric patients
- PMID: 31752566
- PMCID: PMC6882476
- DOI: 10.1080/10717544.2019.1687613
Enhancement of zaleplon oral bioavailability using optimized self-nano emulsifying drug delivery systems and its effect on sleep quality among a sample of psychiatric patients
Abstract
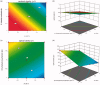
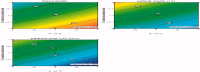
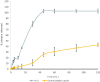
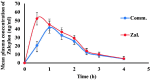
The aim of this work is to develop self-nano emulsifying drug delivery system (SNEDDS) to enhance the oral bioavailability of zaleplon (Zal) as a poorly water-soluble drug. Moreover, the bioavailability and the effect on the quality of sleep among a sample of psychiatric patients is to be assessed. D-optimal mixture design was used for optimization. Optimized SNEDDS formulation was evaluated for droplet size, transmission electron microscope (TEM) and in-vitro dissolution test. Zal bioavailability was evaluated by determining its serum concentration and pharmacokinetic parameters in 8 patients after oral administration. Effect on sleep quality was assessed among 40 psychiatric patients. Patients' sleep quality was assessed in 40 psychiatric patients before and after medication using the Arabic version of the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI). Zal- SNEDDS appeared as nano-sized spherical vesicles. Moreover, Zal was completely dissolved from optimized formulation after 45 min indicating improved dissolution rate. Zal-SNEDDS showed significantly higher Cmax, Tmax and AUC0→∞ compared to commercial product after oral administration. Zal-SNEDDS significantly improved the total score of PSQIs (p < .001) with higher subjective sleep quality, reduced sleep latency, improved day time function and sleep disturbance (p < .001). Using sleep medication was reduced significantly (p = .027). However, it did not modify sleep duration or sleep efficiency. SNEDDS have improved Zal solubility and enhanced its bioavailability. Furthermore, Zal-SNEDDS have improved the total score of PSQIs and may be considered a good choice to enhance the quality of sleep among psychiatric patients.
Keywords: Zaleplon; bioavailability; poorly water-soluble drug and quality of sleep; self-nano emulsifying drug delivery system (SNEDDS).
Figures



References
-
- Abd-Elrasheed E, El-Helaly SN, El-Ashmoony MM, Salah S (2018). Brain targeted intranasal zaleplon nano-emulsion: in-vitro characterization and assessment of gamma aminobutyric acid levels in rabbits' brain and plasma at low and high doses. Curr Drug Deliv 15:898–906. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed OA, Afouna MI, El-Say KM, et al. (2014). Optimization of self-nanoemulsifying systems for the enhancement of in vivo hypoglycemic efficacy of glimepiride transdermal patches. Exp Opin Drug Deliv 11:1005–13. - PubMed
-
- Buysse DJ, Reynolds CF, Monk TH, et al. (1989). The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index: a new instrument for psychiatric practice and research. Psychiatry Res 28:193–213. - PubMed
-
- Date AA, Desai N, Dixit R, Nagarsenker M (2010). Self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems: formulation insights, applications and advances. Nanomedicine 5:1595–616. - PubMed
-
- Doi Y, Minowa M, Uchiyama M, et al. (2000). Psychometric assessment of subjective sleep quality using the Japanese version of the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI-J) in psychiatric disordered and control subjects. Psychiatry Res 97:165–172. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
