Migrating bison engineer the green wave
- PMID: 31754040
- PMCID: PMC6925981
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1913783116
Migrating bison engineer the green wave
Abstract
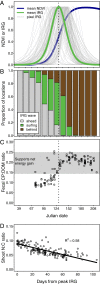
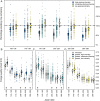
Newly emerging plants provide the best forage for herbivores. To exploit this fleeting resource, migrating herbivores align their movements to surf the wave of spring green-up. With new technology to track migrating animals, the Green Wave Hypothesis has steadily gained empirical support across a diversity of migratory taxa. This hypothesis assumes the green wave is controlled by variation in climate, weather, and topography, and its progression dictates the timing, pace, and extent of migrations. However, aggregate grazers that are also capable of engineering grassland ecosystems make some of the world's most impressive migrations, and it is unclear how the green wave determines their movements. Here we show that Yellowstone's bison (Bison bison) do not choreograph their migratory movements to the wave of spring green-up. Instead, bison modify the green wave as they migrate and graze. While most bison surfed during early spring, they eventually slowed and let the green wave pass them by. However, small-scale experiments indicated that feedback from grazing sustained forage quality. Most importantly, a 6-fold decadal shift in bison density revealed that intense grazing caused grasslands to green up faster, more intensely, and for a longer duration. Our finding broadens our understanding of the ways in which animal movements underpin the foraging benefit of migration. The widely accepted Green Wave Hypothesis needs to be revised to include large aggregate grazers that not only move to find forage, but also engineer plant phenology through grazing, thereby shaping their own migratory movements.
Keywords: bison; grazing lawn; green wave; migration; surfing.
Copyright © 2019 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures


Comment in
-
Mischaracterization of bison migratory patterns in Yellowstone National Park: Consequences for the Green Wave Hypothesis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Apr 28;117(17):9169-9170. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1920842117. Epub 2020 Apr 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32317373 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Reply to Craine: Bison redefine what it means to move to find food.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Apr 28;117(17):9171-9172. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2000713117. Epub 2020 Apr 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32317386 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Fryxell J. M., Sinclair A. R., Causes and consequences of migration by large herbivores. Trends Ecol. Evol. 3, 237–241 (1988). - PubMed
-
- Albon S., Langvatn R., Plant phenology and the benefits of migration in a temperate ungulate. Oikos 65, 502–513 (1992).
-
- Fryxell J. M., Wilmshurst J. F., Sinclair A. R., Predictive models of movement by Serengeti grazers. Ecology 85, 2429–2435 (2004).
-
- Boone R. B., Thirgood S. J., Hopcraft J. G. C., Serengeti wildebeest migratory patterns modeled from rainfall and new vegetation growth. Ecology 87, 1987–1994 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Hebblewhite M., Merrill E., McDermid G., A multi-scale test of the forage maturation hypothesis in a partially migratory ungulate population. Ecol. Monogr. 78, 141–166 (2008).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

