Menopausal Acne - Challenges And Solutions
- PMID: 31754313
- PMCID: PMC6825478
- DOI: 10.2147/IJWH.S174292
Menopausal Acne - Challenges And Solutions
Abstract
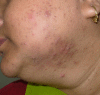
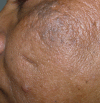
Although acne is a disease predominant in adolescence, it is being increasingly observed in adult life, including the menopausal period. The etiology of menopausal acne is multifactorial, with hormonal imbalance being the major culprit. There is a relative increase of androgens in the menopausal female that leads to clinical hyperandrogenism manifesting as acne, hirsutism and androgenetic alopecia. Other endocrine disorders including thyroid abnormalities, hyperprolactinemia and insulin resistance also play a role. Genetics, stress, dietary changes, lack of sleep and exercise and other lifestyle changes are implicated as trigger factors. Most menopausal women with isolated few acne lesions have normoandrogenic serum levels and do not require extensive investigations. However, baseline investigations including total testosterone are useful. Patients must also be evaluated for associated comorbidities such as obesity, diabetes, hypertension and dyslipidemia. A detailed history can help to exclude polycystic ovarian syndrome, late-onset congenital adrenal hyperplasia or medications as a cause of acne. The evaluation of menopausal acne and the approach to treatment depend on the severity of acne and associated features. In patients with mild acne without virilization, prolonged topical therapy is the mainstay of treatment. Though combined oral contraceptives are effective, they are relatively contraindicated in the postmenopausal period. Spironolactone is the first choice of therapy in the subset of patients that require oral anti-androgen therapy. Procedural treatment can be useful as it can also help in the treatment of associated acne scars and concomitant skin aging. It is also important to focus on lifestyle changes such as reducing stress, controlling obesity, having a healthy diet, exercise and proper skin care routine to reduce acne. The focus of this article is on the clinical presentation and management challenges of menopausal acne, which represents a special subtype of acne.
Keywords: acne; adult; hormonal; hyperandrogenism; menopause.
© 2019 Khunger and Mehrotra.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
AMERICAN ASSOCIATION OF CLINICAL ENDOCRINOLOGISTS, AMERICAN COLLEGE OF ENDOCRINOLOGY, AND ANDROGEN EXCESS AND PCOS SOCIETY DISEASE STATE CLINICAL REVIEW: GUIDE TO THE BEST PRACTICES IN THE EVALUATION AND TREATMENT OF POLYCYSTIC OVARY SYNDROME--PART 1.Endocr Pract. 2015 Nov;21(11):1291-300. doi: 10.4158/EP15748.DSC. Endocr Pract. 2015. PMID: 26509855
-
Androgen dependence of hirsutism, acne, and alopecia in women: retrospective analysis of 228 patients investigated for hyperandrogenism.Medicine (Baltimore). 2009 Jan;88(1):32-45. doi: 10.1097/md.0b013e3181946a2c. Medicine (Baltimore). 2009. PMID: 19352298
-
Acne: effect of hormones on pathogenesis and management.Am J Clin Dermatol. 2002;3(8):571-8. doi: 10.2165/00128071-200203080-00007. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2002. PMID: 12358558 Review.
-
Approach to Investigation of Hyperandrogenism in a Postmenopausal Woman.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2023 Apr 13;108(5):1243-1253. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgac673. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2023. PMID: 36409990 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Hyperandrogenism, adrenal dysfunction, and hirsutism].Hautarzt. 2020 Oct;71(10):752-761. doi: 10.1007/s00105-020-04677-1. Hautarzt. 2020. PMID: 32857168 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Pattern of Skin Diseases at a Dermatology Center: A Retrospective Study.Cureus. 2024 Jul 24;16(7):e65259. doi: 10.7759/cureus.65259. eCollection 2024 Jul. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39184705 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the Nuances of Adult Female Acne: A Comprehensive Exploration of Epidemiology, Treatment Modalities, Dermocosmetics, and the Menopausal Influence.Int J Womens Health. 2024 Apr 18;16:663-678. doi: 10.2147/IJWH.S431523. eCollection 2024. Int J Womens Health. 2024. PMID: 38650835 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Menopausal Transition: Is the Hair Follicle "Going through Menopause"?Biomedicines. 2023 Nov 14;11(11):3041. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11113041. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 38002043 Free PMC article.
-
Menopause, skin and common dermatoses. Part 2: skin disorders.Clin Exp Dermatol. 2022 Dec;47(12):2117-2122. doi: 10.1111/ced.15308. Epub 2022 Oct 26. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2022. PMID: 35727900 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Association Between Short-Term Air Pollution Exposure and Post-Adolescent Acne: The Evidence from a Time Series Analysis in Xi'an, China.Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2021 Jun 25;14:723-731. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S320248. eCollection 2021. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 34211290 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Goulden V, Stables GI, Cunliffe WJ. The prevalence of facial acne in adults. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;41:577–580. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources