LncRNA H19 ameliorates myocardial infarction-induced myocardial injury and maladaptive cardiac remodelling by regulating KDM3A
- PMID: 31755219
- PMCID: PMC6933349
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.14846
LncRNA H19 ameliorates myocardial infarction-induced myocardial injury and maladaptive cardiac remodelling by regulating KDM3A
Erratum in
-
LncRNA H19 ameliorates myocardial infarction-induced myocardial injury and maladaptive cardiac remodelling by regulating KDM3A.J Cell Mol Med. 2023 Jun;27(12):1757-1760. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17753. J Cell Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37325951 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
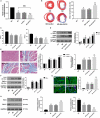
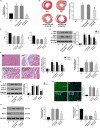
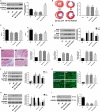
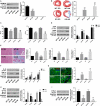
Myocardial infarction (MI) remains the leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, and novel therapeutic targets still need to be investigated to alleviate myocardial injury and the ensuing maladaptive cardiac remodelling. Accumulating studies have indicated that lncRNA H19 might exert a crucial regulatory effect on cardiovascular disease. In this study, we aimed to explore the biological function and molecular mechanism of H19 in MI. To investigate the biological functions of H19, miRNA-22-3p and KDM3A, gain- and loss-of-function experiments were performed. In addition, bioinformatics analysis, dual-luciferase reporter assays, RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) assays, RNA pull-down assays, quantitative RT-PCR and Western blot analyses as well as rescue experiments were conducted to reveal an underlying competitive endogenous RNA (ceRNA) mechanism. We found that H19 was significantly down-regulated after MI. Functionally, enforced H19 expression dramatically reduced infarct size, improved cardiac performance and alleviated cardiac fibrosis by mitigating myocardial apoptosis and decreasing inflammation. However, H19 knockdown resulted in the opposite effects. Bioinformatics analysis and dual-luciferase assays revealed that, mechanistically, miR-22-3p was a direct target of H19, which was also confirmed by RIP and RNA pull-down assays in primary cardiomyocytes. In addition, bioinformatics analysis and dual-luciferase reporter assays also demonstrated that miRNA-22-3p directly targeted the KDM3A gene. Moreover, subsequent rescue experiments further verified that H19 regulated the expression of KDM3A to ameliorate MI-induced myocardial injury in a miR-22-3p-dependent manner. The present study revealed the critical role of the lncRNAH19/miR-22-3p/KDM3A pathway in MI. These findings suggest that H19 may act as a potential biomarker and therapeutic target for MI.
Keywords: KDM3A; LncRNA H19; miR-22-3p; myocardial infarction.
© 2019 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Hristov M, Weber C. Myocardial infarction and inflammation: lost in the biomarker labyrinth. Circ Res. 2015;116(5):781‐783. - PubMed
-
- Thiele H, Ohman EM, de Waha‐Thiele S, et al. Management of cardiogenic shock complicating myocardial infarction: an update 2019. Eur Heart J. 2019;40(32):2671‐2683. - PubMed
-
- Shah M, Patil S, Patel B, et al. Causes and predictors of 30‐day readmission in patients with acute myocardial infarction and cardiogenic shock. Circ Heart Fail. 2018;11(4):e004310. - PubMed
-
- Mahmoud KD, Zijlstra F. Thrombus aspiration in acute myocardial infarction. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2016;13(7):418‐428. - PubMed
-
- Toldo S, Abbate A. The NLRP3 inflammasome in acute myocardial infarction. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2018;15(4):203‐214. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

