Retinol binding protein IV purified from Escherichia coli using intein-mediated cleavage as a suitable replacement for serum sources
- PMID: 31756375
- PMCID: PMC6941568
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pep.2019.105542
Retinol binding protein IV purified from Escherichia coli using intein-mediated cleavage as a suitable replacement for serum sources
Abstract
Retinol binding protein IV (RBP) functions as the principal carrier of retinol (Vitamin A) in the blood, where RBP circulates bound to another serum protein, transthyretin. Isolation of pure RBP from the transthyretin complex in human serum can be difficult, but expression of RBP in recombinant systems can circumvent these purification issues. Human recombinant RBP has previously been successfully expressed and purified from E. coli, but recovery of active protein typically requires extensive processing steps, such as denaturing and refolding, and complex purification steps, such as multi-modal chromatography. Furthermore, these methods produce recombinant proteins, often tagged, that display different functional and structural characteristics across systems. In this work, we optimized downstream processing by use of an intein-based expression system in E. coli to produce tag-free, human recombinant RBP (rRBP) with intact native amino termini at yields of up to ~15 mg/L off column. The novel method requires solubilization of inclusion bodies and subsequent oxidative refolding in the presence of retinol, but importantly allows for one-step chromatographic purification that yields high purity rRBP with no N-terminal Met or other tag. Previously reported purification methods typically require two or more chromatographic separation steps to recover tag-free rRBP. Given the interest in mechanistic understanding of RBP transport of retinol in health and disease, we characterized our purified product extensively to confirm rRBP is both structurally and functionally a suitable replacement for serum-derived RBP.
Keywords: Inteins; Oxidative refolding; Retinol; Retinol binding protein; Transthyretin.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



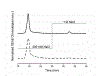



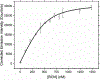

References
-
- Zanotti G and Berni R, Plasma retinol-binding protein: Structure and interactions with retinol, retinoids, and transthyretin. Vitamins and Hormones - Advances in Research and Applications, Vol 69, 2004. 69: p. 271–295. - PubMed
-
- Newcomer ME and Ong DE, Plasma retinol binding protein: structure and function of the prototypic lipocalin. Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta-Protein Structure and Molecular Enzymology, 2000. 1482(1–2): p. 57–64. - PubMed
-
- Perduca M, et al., Human plasma retinol-binding protein (RBP4) is also a fatty acid-binding protein. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids, 2018. 1863(4): p. 458–466. - PubMed
-
- Goodman DS, Vitamin A and retinoids in health and disease. N Engl J Med, 1984. 310(16): p. 1023–31. - PubMed
-
- Makover A, et al., Localization of retinol-binding protein messenger RNA in the rat kidney and in perinephric fat tissue. J Lipid Res, 1989. 30(2): p. 171–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

