Evaluation of the regulatory model for Ni2+ sensing by Nur from Streptomyces coelicolor
- PMID: 31756557
- PMCID: PMC7012763
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2019.110859
Evaluation of the regulatory model for Ni2+ sensing by Nur from Streptomyces coelicolor
Abstract
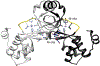
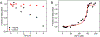
Streptomyces coelicolor is a soil-dwelling bacterium that is medically important due to its ability to produce several antibiotics, and nickel accumulation within this organism has been shown to prevent the production of the antibiotic undecylprodigiosin. The transcriptional repressor important in regulation of nickel uptake is the homodimeric Nur, a member of the Fur family. Nur contains two metal-binding sites per monomer: the M-site and the Ni-site. The work described here seeks to determine the roles of each of the metal-binding sites to establish a model of Nur activity through mutational studies, metal titrations, and fluorescence anisotropy. Through these studies, a model of Nur activity is proposed in which femtomolar metal binding to one M-site of Nur prompts DNA-binding, and metal binding to the second M-site fully activates the protein. Evidence is provided that shows cooperative metal binding to the Ni-site, but this process dampens affinity for promoter DNA.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
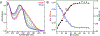


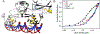
References
-
- Mulrooney SB, Hausinger RP, Nickel uptake and utilization by microorganisms., FEMS Microbiol. Rev 27 (2003) 239–261. - PubMed
-
- Stohs SJ, Bagchi D, Oxidative mechanisms in the toxicity of metal ions., Free Radic. Biol. Med 18 (1995) 321–336. - PubMed
-
- Abbas AS, Edwards C, Effects of Metals on Streptomyces coelicolor Growth and Actinorhodin Production, Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 56 (1990) 675–680. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC183404/. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

