Novel ACE inhibitory tripeptides from ovotransferrin using bioinformatics and peptidomics approaches
- PMID: 31758024
- PMCID: PMC6874687
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-53964-y
Novel ACE inhibitory tripeptides from ovotransferrin using bioinformatics and peptidomics approaches
Abstract
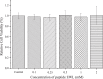
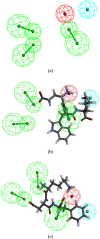
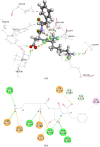
Food-derived ACE inhibitory peptides have recently attracted increased attention. This work focused on a more efficient in silico method to find ACE inhibitory peptides from ovotransferrin. In this work, ovotransferrin was digested into peptides by virtual enzymolysis. Subsequently, in vitro ACE inhibitory activity of potential tripeptides was conducted following the peptide score, toxicity, and water solubility prediction. Both pharmacophore study and flexible docking were applied to analyze ACE inhibition mechanism of tripeptides. Our results demonstrated that EWL was a potent ACE inhibitory tripeptide with IC50 value of 380 ± 10 μM. Besides, pharmacophore and flexible docking showed that the pi interaction and hydrogen bond were the key interactions in ACE-EWL complex. It appears that the in vitro ACE inhibitory activity of tripeptide EWL was consistent with its molecular modeling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Bougatef A, et al. Angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory activities of sardinelle (Sardinella aurita) by-products protein hydrolysates obtained by treatment with microbial and visceral fish serine proteases. Food Chemistry. 2008;111:350–356. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.03.074. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

