Italy's health performance, 1990-2017: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017
- PMID: 31759893
- PMCID: PMC7098474
- DOI: 10.1016/S2468-2667(19)30189-6
Italy's health performance, 1990-2017: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017
Abstract
Background: Through a comprehensive analysis of Italy's estimates from the Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors Study (GBD) 2017, we aimed to understand the patterns of health loss and response of the health-care system, and offer evidence-based policy indications in light of the demographic transition and government health spending in the country.
Methods: Estimates for Italy were extracted from GBD 2017. Data on Italy are presented for 1990 and 2017, on prevalence, causes of death, years of life lost, years lived with disability, disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs), life expectancy at birth and at age 65 years, healthy life expectancy, and Healthcare Access and Quality (HAQ) Index. We compared the estimates for Italy with those of 15 other western European countries.
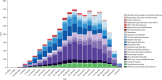
Findings: The quality of the universal health system and healthy behaviours contribute to favourable overall health, even in comparison with other western European countries. In 2017, life expectancy and HAQ Index score in Italy were among the highest globally, with life expectancy at birth reaching 85·3 years for females and 80·8 for males in 2017, ranking Italy eighth globally for females and sixth for males, and an HAQ Index score of 94·9 in 2016 compared with 81·54 in 1990, keeping Italy ranked as ninth globally. Between 1990 and 2017 age-standardised death rates for cardiovascular diseases decreased by 53·7% (95% uncertainty interval -56·1 to -51·4), for neoplasms decreased by 28·2% (-32·3 to -24·6), and for transport injuries decreased by 62·1% (-64·6 to -59·2). However, population ageing is causing an increase in the burden of specific diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease and other dementias (DALYs increased by 77·9% [68·4 to 87·2]) and pancreatic (DALYs increased by 39·7% [28·4 to 51·7]) and uterine cancers (DALYs increased by 164·7% [129·7 to 202·5]). Behavioural risk factors, which are potentially modifiable, still have a strong effect, particularly on cardiovascular diseases and neoplasms. For instance, in 2017, 44 400 (41 200 to 47 800) cancer deaths were attributed to smoking, 12 000 (9600 to 14 800) to alcohol use, and 9500 (5400 to 14 200) to high body-mass index, while 47 000 (31 100 to 65 700) deaths due to cardiovascular diseases could be attributed to high LDL cholesterol, 28 700 (19 700 to 38 500) to diets low in whole grains, and 15 900 (8500 to 24 900) to low physical activity.
Interpretation: Italy provides an interesting example of the results that can be achieved by a mix of relatively healthy lifestyles and a universal health system. Two main issues require attention, population ageing and gradual decrease of public health financing, which both pose several challenges to the future of Italy's health status. Our findings should be useful to Italy's policy makers and health system experts elsewhere.
Funding: Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation.
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd. This is an Open Access article under the CC BY 4.0 license. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures

Comment in
-
Health and the effect of universal health coverage in Italy.Lancet Public Health. 2019 Dec;4(12):e597-e598. doi: 10.1016/S2468-2667(19)30206-3. Epub 2019 Nov 20. Lancet Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31759895 No abstract available.
References
-
- Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development/European Observatory on Health Systems and Policies . Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development Publishing, European Observatory on Health Systems and Policies; Paris, Brussels: 2017. Italy: country health profile 2017, state of health in the EU.
-
- Lu W, Del Giudice V. Bloomberg; March 20, 2017. Italy's struggling economy has world's healthiest people.https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2017-03-20/italy-s-struggling-ec...
-
- Legge 23 Dicembre 1978, n.833: istituzione del servizio sanitario nazionale. Gazzetta Ufficiale, Dec 28, 1978: serie generale 360. http://www.gazzettaufficiale.it/eli/gu/1978/12/28/360/so/0/sg/pdf

