Association between atopic disease and anemia in pediatrics: a cross-sectional study
- PMID: 31760939
- PMCID: PMC6876088
- DOI: 10.1186/s12887-019-1836-5
Association between atopic disease and anemia in pediatrics: a cross-sectional study
Abstract
Background: Atopic diseases, such as atopic dermatitis, allergic rhinitis, and asthma, are inflammatory diseases common in pediatric patients. This study investigated whether these inflammatory atopic diseases were associated with anemia in pediatrics.
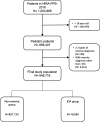
Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted using a pediatric dataset from the Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service (HIRA) of South Korea in 2016. Multivariable logistic regression, adjusting for demographic covariates was used for analyse the association between atopic disease and iron deficiency anemia (IDA).
Results: A total of 846,718 pediatric patients were included in the study. Of these, 19,594 (2.31%) had a diagnosis of IDA. The logistic regression analyses including covariates revealed there were association between atopic disease and IDA. The adjusted OR (aOR) of IDA was 1.42 (95% CI, 1.37-1.47) for atopic dermatitis, 1.25 (95% CI, 1.21-1.29) for allergic rhinitis, and 1.71 (95% CI, 1.65-1.76) for asthma. IDA was more prevalent in patients with multiple comorbid atopic diseases, with aOR of 1.30 (95% CI, 1.25-1.35), 1.81 (95% CI, 1.73-1.89), and 2.58 (95% CI, 2.43-2.73) for 1, 2, or 3 atopic diagnoses. There was no evidence of multicollinearity among covariates.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that atopic disease was associated with IDA. Further study is needed to clarify the distinction between IDA and/or AI to better understand the cause of anemia in patients with inflammatory diseases.
Keywords: Allergic rhinitis; Anemia; Asthma; Atopic dermatitis; Atopic disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical