RNase H2-RED carpets the path to eukaryotic RNase H2 functions
- PMID: 31761672
- PMCID: PMC6936605
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2019.102736
RNase H2-RED carpets the path to eukaryotic RNase H2 functions
Abstract
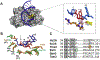
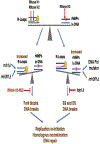
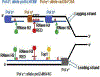
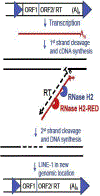
Eukaryotic RNases H2 have dual functions in initiating the removal of ribonucleoside monophosphates (rNMPs) incorporated by DNA polymerases during DNA synthesis and in cleaving the RNA moiety of RNA/DNA hybrids formed during transcription and retrotransposition. The other major cellular RNase H, RNase H1, shares the hybrid processing activity, but not all substrates. After RNase H2 incision at the rNMPs in DNA the Ribonucleotide Excision Repair (RER) pathway completes the removal, restoring dsDNA. The development of the RNase H2-RED (Ribonucleotide Excision Defective) mutant enzyme, which can process RNA/DNA hybrids but is unable to cleave rNMPs embedded in DNA has unlinked the two activities and illuminated the roles of RNase H2 in cellular metabolism. Studies mostly in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, have shown both activities of RNase H2 are necessary to maintain genome integrity and that RNase H1 and H2 have overlapping as well as distinct RNA/DNA hybrid substrates. In mouse RNase H2-RED confirmed that rNMPs in DNA during embryogenesis induce lethality in a p53-dependent DNA damage response. In mammalian cell cultures, RNase H2-RED helped identifying DNA lesions produced by Top1 cleavage at rNMPs and led to determine that RNase H2 participates in the retrotransposition of LINE-1 elements. In this review, we summarize the studies and conclusions reached by utilization of RNase H2-RED enzyme in different model systems.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

