Sepsis patient evaluation emergency department (SPEED) score & mortality in emergency department sepsis (MEDS) score in predicting 28-day mortality of emergency sepsis patients
- PMID: 31761698
- PMCID: PMC6921192
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cjtee.2019.10.004
Sepsis patient evaluation emergency department (SPEED) score & mortality in emergency department sepsis (MEDS) score in predicting 28-day mortality of emergency sepsis patients
Abstract
Purpose: Sepsis is a common acute life-threatening condition that emergency physicians routinely face. Diagnostic options within the Emergency Department (ED) are limited due to lack of infrastructure, consequently limiting the use of invasive hemodynamic monitoring or imaging tests. The mortality rate due to sepsis can be assessed via multiple scoring systems, for example, mortality in emergency department sepsis (MEDS) score and sepsis patient evaluation in the emergency department (SPEED) score, both of which quantify the variation of mortality rates according to clinical findings, laboratory data, or therapeutic interventions. This study aims to improve the management processes of sepsis patients by comparing SPEED score and MEDS score for predicting the 28-day mortality in cases of emergency sepsis.
Methods: The study is a cross-sectional, prospective study including 61 sepsis patients in ED in Suez Canal University Hospital, Egypt, from August 2017 to June 2018. Patients were selected by two steps: (1) suspected septic patients presenting with at least one of the following abnormal clinical findings: (a) body temperature higher than 38 °C or lower than 36 °C, (b) heart rate higher than 90 beats/min, (c) hyperventilation evidenced by respiratory rate higher than 20 breaths/min or PaCO2 lower than 32 mmHg, and (d) white blood cell count higher than 12,000/μL or lower than 4000/μL; (2) confirmed septic patients with at least a 2-point increase from the baseline total sequential organ failure assessment (SOFA) score following infection. Other inclusion criteria included adult patients with an age ≥18 years regardless of gender and those who had either systemic inflammatory response syndrome or suspected/confirmed infection. Patients were shortly follow-up for the 28-day mortality. Each patient was subject to SPEED score and MEDS score and then the results were compared to detect which of them was more effective in predicting outcome. The receiver operating characteristic curves were also done for MEDS and SPEED scores.
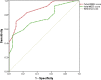
Results: Among the 61 patients, 41 died with the mortality rate of 67.2%. The mortality rate increased with a higher SPEED and MEDS scores. Both SPEED and MEDS scores revealed significant difference between the survivors and nonsurvivors (p = 0.004 and p < 0.001, respectively), indicating that both the two systems are effective in predicting the 28-day mortality of sepsis patients. Thereafter, the receiver operating characteristic curves were plotted, which showed that SPEED was better than the MEDS score when applied to the complete study population with an area under the curve being 0.87 (0.788-0.963) as compared with 0.75 (0.634-0.876) for MEDS. Logistic regression analysis revealed that the best fitting predictor of 28-day mortality for sepsis patients was the SPEED scoring system. For every one unit increase in SPEED score, the odds of 28-day mortality increased by 37%.
Conclusion: SPEED score is more useful and accurate than MEDS score in predicting the 28-day mortality among sepsis patients. Therefore SPEED rather than MEDS should be more widely used in the ED for sepsis patients.
Keywords: Mortality; Mortality in emergency department sepsis score; Sepsis; Sepsis patient evaluation emergency department score.
Copyright © 2019 Chinese Medical Association. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Torio C.M., Moore B.J. National inpatient hospital costs: the most expensive conditions by payer. Healthc Cost Util Proj (HCUP) Stat Briefs. 2013 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK368492/ - PubMed
-
- Cohen J., Vincent J.L., Adhikari N.K. Sepsis: a roadmap for future research. Lancet Infect Dis. 2015;15:581–614. - PubMed
-
- Bennett J.E., Dolin R., Blaser M.J. Elsevier Health Sciences; London: 2009. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases.
-
- Levy M.M., Fink M.P., Marshall J.C. SCCM/ESICM/ACCP/ATS/SIS international sepsis definitions conference. Crit Care Med. 2001;31(2003):1250–1256. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical