TH1/TH2 chemokines/cytokines profile in rats treated with tetanus toxoid and Euphorbia tirucalli
- PMID: 31762649
- PMCID: PMC6864399
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2018.08.005
TH1/TH2 chemokines/cytokines profile in rats treated with tetanus toxoid and Euphorbia tirucalli
Abstract
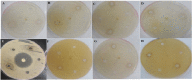
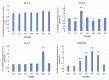
Natural products, including their purified materials, play a remarkable role in drug development. The Euphorbiaceae family, mainly Euphorbia tirucalli, is used in some traditional medicine, and has evidence that its latex comprises immunomodulatory properties and cytokine production. This study aimed to measure the in vivo production of chemokines (IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-12, and RANTES), TH1 cytokines (IFN-γ, TNF-α, GM-CSF, and IL-2) and TH2 cytokines (IL-4, IL-6, IL-10, and IL-13) in rats after treatments with ethanol latex extract of E. tirucalli. Vaccine treated and untreated rats were divided into seven groups to assess antimicrobial activities of the extracted components. After completion of the treatment schedule, blood was withdrawn and sera were collected. The results showed that the main component of the extract was a euphol compound. The extract showed antimicrobial activity and had the ability to modulate innate and adaptive immunity. Animals treated with extract for only 7 days before vaccination showed higher levels of antibody production. The extract showed antibacterial and antifungal activities. The extract could stimulate both adaptive and innate immunity. Pre-treatment with the extract increased immune responses in vaccinated animals, indicating the usefulness of the extract before immunization.
Keywords: Cytokines; Euphorbia tirucalli; Immunity; Plant extract; Tetanus vaccine.
© 2018 Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of King Saud University.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Analytical methods to access the chemical composition of an Euphorbia tirucalli anticancer latex from traditional Brazilian medicine.J Ethnopharmacol. 2019 Jun 12;237:255-265. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.03.041. Epub 2019 Mar 27. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30928500
-
Consumption of latex from Euphorbia tirucalli L. promotes a reduction of tumor growth and cachexia, and immunomodulation in Walker 256 tumor-bearing rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Jun 12;255:112722. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112722. Epub 2020 Feb 28. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32114165
-
Antifungal activity against Cryptococcus neoformans strains and genotoxicity assessment in human leukocyte cells of Euphorbia tirucalli L.Braz J Microbiol. 2015 Mar 4;45(4):1349-55. doi: 10.1590/s1517-83822014000400027. eCollection 2014. Braz J Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25763040 Free PMC article.
-
[Up-to-date understanding of tuberculosis immunity].Kekkaku. 2003 Jan;78(1):51-5. Kekkaku. 2003. PMID: 12683337 Review. Japanese.
-
Role of interferons and other cytokines in the regulation of the immune response.APMIS. 1995 Mar;103(3):161-79. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1995.tb01092.x. APMIS. 1995. PMID: 7538771 Review.
Cited by
-
CD3D: a prognostic biomarker associated with immune infiltration and immunotherapeutic response in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Bioengineered. 2022 May;13(5):13784-13800. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2084254. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35712757 Free PMC article.
-
Terpenoids, Cannabimimetic Ligands, beyond the Cannabis Plant.Molecules. 2020 Mar 29;25(7):1567. doi: 10.3390/molecules25071567. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32235333 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adkins B., Leclerc C., Marshall-Clarke S. Neonatal adaptive immunity comes of age. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004;4:553. - PubMed
-
- Allan S.M., Tyrrell P.J., Rothwell N.J. Interleukin-1 and neuronal injury. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005;5:629. - PubMed
-
- Appendino G., Szallasi A. Euphorbium: modern research on its active principle, resiniferatoxin, revives an ancient medicine. Life Sci. 1997;60:681–696. - PubMed
-
- Arend W.P., Palmer G., Gabay C. IL-1, IL-18, and IL-33 families of cytokines. Immunol. Rev. 2008;223:20–38. - PubMed
-
- Arulanandam B.P., Mittler J.N., Lee W.T., O’Toole M., Metzger D.W. Neonatal administration of IL-12 enhances the protective efficacy of antiviral vaccines. J. Immunol. 2000;164:3698–3704. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

