Impact of quercetin on tight junctional proteins and BDNF signaling molecules in hippocampus of PCBs-exposed rats
- PMID: 31762681
- PMCID: PMC6853011
- DOI: 10.2478/intox-2018-0029
Impact of quercetin on tight junctional proteins and BDNF signaling molecules in hippocampus of PCBs-exposed rats
Abstract
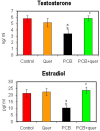
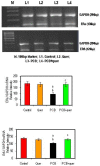
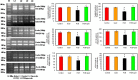
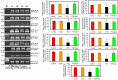
Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) consist of a range of toxic substances which are directly proportional to carcinogenesis and tumor-promoting factors as well as having neurotoxic properties. Reactive oxygen species, which are produced from PCBs, alter blood-brain barrier (BBB) integrity, which is paralleled by cytoskeletal rearrangements and redistribution and disappearance of tight junction proteins (TJPs) like claudin-5 and occludin. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), plays an important role in the maintenance, survival of neurons and synaptic plasticity. It is predominant in the hippocampal areas vital to learning, memory and higher thinking. Quercetin, a flavonoid, had drawn attention to its neurodefensive property. The study is to assess the role of quercetin on serum PCB, estradiol and testosterone levels and mRNA expressions of estrogen receptor α and β, TJPs and BDNF signaling molecules on the hippocampus of PCBs-exposed rats. Rats were divided into 4 groups of 6 each. Group I rats were intraperitoneally (i.p.) administered corn oil (vehicle). Group II received quercetin 50 mg/kg/bwt (gavage). Group III received PCBs (Aroclor 1254) at 2 mg/kg bwt (i.p). Group IV received quercetin 50 mg/kg bwt (gavage) simultaneously with PCBs 2 mg/kg bwt (i.p.). The treatment was given daily for 30 days. The rats were euthanized 24 h after the experimental period. Blood was collected for quantification of serum PCBs estradiol and testosterone. The hippocampus was dissected and processed for PCR and Western blot; serum PCB was observed in PCB treated animals, simultaneously quercetin treated animals showed PCB metabolites. Serum testosterone and estradiol were decreased after PCB exposure. Quercetin supplementation brought back normal levels. mRNA expressions of estrogen α and β were decreased in the hippocampus of PCB treated rats. TJPS and BDNF signalling molecules were decreased in hippocampus of PCB treated rats. Quercetin supplementation retrieved all the parameters. Quercetin alone treated animals showed no alteration. Thus in PCB caused neurotoxicity, quercetin protects and prevents neuronal damage in the hippocampus.
Keywords: BDNF; GC-MS; PCBs; Quercetin; TJPs.
Copyright © 2018 SETOX & Institute of Experimental Pharmacology and Toxicology, SASc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Polychlorinated biphenyls impair blood-brain barrier integrity via disruption of tight junction proteins in cerebrum, cerebellum and hippocampus of female Wistar rats: neuropotential role of quercetin.Hum Exp Toxicol. 2013 Jul;32(7):706-20. doi: 10.1177/0960327112464798. Epub 2012 Nov 15. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 23155198
-
Polychlorinated biphenyls induced oxidative stress mediated neurodegeneration in hippocampus and behavioral changes of adult rats: anxiolytic-like effects of quercetin.Toxicol Lett. 2013 Sep 12;222(1):45-54. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2013.06.237. Epub 2013 Jul 4. Toxicol Lett. 2013. PMID: 23831945
-
Polychlorinated biphenyl (PCBs)-induced oxidative stress plays a critical role on cerebellar dopaminergic receptor expression: ameliorative role of quercetin.Neurotox Res. 2012 Feb;21(2):149-59. doi: 10.1007/s12640-011-9253-z. Epub 2011 Jul 12. Neurotox Res. 2012. PMID: 21748531
-
Effects of polychlorinated biphenyls on the nervous system.Toxicol Ind Health. 2000 Sep;16(7-8):305-33. doi: 10.1177/074823370001600708. Toxicol Ind Health. 2000. PMID: 11693948 Review.
-
Neurochemical effects of polychlorinated biphenyls: an overview and identification of research needs.Neurotoxicology. 1997;18(3):727-43. Neurotoxicology. 1997. PMID: 9339820 Review.
Cited by
-
Quercetin Abrogates Oxidative Neurotoxicity Induced by Silver Nanoparticles in Wistar Rats.Life (Basel). 2022 Apr 13;12(4):578. doi: 10.3390/life12040578. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35455069 Free PMC article.
-
The Potential Role of Polyphenols in Oxidative Stress and Inflammation Induced by Gut Microbiota in Alzheimer's Disease.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Aug 27;10(9):1370. doi: 10.3390/antiox10091370. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34573002 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Flavonoid on the Brain: Quercetin as a Potential Therapeutic Agent in Central Nervous System Disorders.Life (Basel). 2022 Apr 15;12(4):591. doi: 10.3390/life12040591. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35455082 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exposure to polychlorinated biphenyls selectively dysregulates endothelial circadian clock and endothelial toxicity.J Hazard Mater. 2023 Jul 15;454:131499. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.131499. Epub 2023 Apr 26. J Hazard Mater. 2023. PMID: 37126901 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing BDNF Signaling to Promote Resilience in Aging.Aging Dis. 2024 Sep 3;16(4):1813-1841. doi: 10.14336/AD.2024.0961. Aging Dis. 2024. PMID: 39656488 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anbalagan J, Kanagaraj P, Srinivasan N, Aruldhas MM, Arunakaran J. Effect of polychlorinated biphenyl, Aroclor 1254 on rat epididymis. Indian J Med Res. 2003;118:236–42. - PubMed
-
- Andersen JK. Oxidative stress in neurodegeneration: cause or consequence? Nat Med. 2004;10(Suppl):S18–25. - PubMed
-
- Andric SA, Kostic TS, Stojilkovic SS, Kovacevic RZ. Inhibition of rat testicular androgenesis by a polychlorinated biphenyl mixture aroclor 1248. Biol Reprod. 2000;62(6):1882–8. - PubMed
-
- Awad HM, Boersma MG, Vervoort J, Rietjens IM. Peroxidase-catalyzed formation of quercetin quinone methide-glutathione adducts. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2000;378(2):224–33. - PubMed
-
- Bancroft LW, Peterson JJ, Kransdorf MJ, Nomikos GC, Murphey MD. Soft tissue tumors of the lower extremities. Radiol Clin North Am. 2002;40(5):991–1011. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
