Plan quality comparison for cervical carcinoma treated with Halcyon and Trilogy intensity-modulated radiotherapy
- PMID: 31762823
- PMCID: PMC6856582
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.32500
Plan quality comparison for cervical carcinoma treated with Halcyon and Trilogy intensity-modulated radiotherapy
Abstract
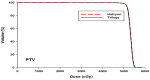
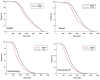
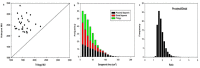
Purpose: Varian Halcyon is a novel machine with dual-layer leaves, single flattening filter free (FFF) energy and an enclosed bore. The purpose of this study was to compare the differences in dosimetry and plan parameters of intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) plans between the Halcyon and Trilogy accelerators. Methods and Materials: A total of 30 IMRT plans from cervical carcinoma patients were retrospectively analyzed on the Trilogy and Eclipse v13.5 treatment planning systems (TPSs). For each patient, a new plan based on Halcyon was created with the same planning parameters and optimization constraints using the Eclipse Version 15.1 TPS. To compare plan qualities, dosimetry parameters regarding planning target volume (PTV), organs at risk (OARs), monitor unit (MU) efficiency, segment size and treatment time were evaluated. Evaluation of the helical diode array system was performed with gamma-index analysis. Results: The dose distribution of the target volume of the Halcyon and Trilogy plans showed no significant difference (p > 0.05). The mean doses of rectum and both femoral heads for Halcyon plans were significantly reduced compared to those for Trilogy plans (p < 0.05). Compared to Trilogy, Halcyon increased the number of MUs from 1542.9±248.3 MU to 2514.9±328.2 MU (p = 0.00) and decreased the delivery time from 11.28±1.36 min to 3.26±0.26 min (p = 0.00). The average segment areas of Halcyon plans for proximal and distal multileaf collimators (MLCs) were 42.1 ± 31.2 cm2 and 28.4 ± 23.7 cm2, respectively, and that of Trilogy plans was 27.3 ± 16.9 cm2. The mean gamma index (3 mm/3%) results for the Halcyon and Trilogy plans were 99.41±0.26 and 99.76±0.32 (p > 0.05), respectively. Conclusions: All Halcyon treatment plans were recognized as clinically acceptable and had statistically better OAR sparing with higher delivery efficiency. The Halcyon system exhibited fast treatment delivery of IMRT with good dosimetric agreement using ArcCHECK.
Keywords: Dual-layer MLC; Flattening filter free; Intensity-modulated radiotherapy; Segment area.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Treatment planning comparison of volumetric modulated arc therapy with the trilogy and the Halcyon for bilateral breast cancer.Radiat Oncol. 2021 Feb 18;16(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s13014-021-01763-z. Radiat Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33602267 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Multi-leaf Collimator Parameters on Head and Neck Plan Quality and Delivery: A Comparison between Halcyon™ and Truebeam® Treatment Delivery Systems.Cureus. 2018 Nov 28;10(11):e3648. doi: 10.7759/cureus.3648. Cureus. 2018. PMID: 30723647 Free PMC article.
-
Volumetric modulated arc therapy for hippocampal-sparing prophylactic cranial irradiation: Planning comparison of Halcyon and C-arm accelerators.Front Oncol. 2023 Mar 7;13:993809. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.993809. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36959800 Free PMC article.
-
Dosimetry study of nasopharyngeal carcinoma based on Halcyon accelerator fixed-field intensity-modulated radiation therapy.J Cancer Res Ther. 2021 Nov;17(5):1165-1171. doi: 10.4103/jcrt.jcrt_992_21. J Cancer Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 34850763
-
Dosimetric performance evaluation of the Halcyon treatment platform for stereotactic radiotherapy: A pooled study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Sep 8;102(36):e34933. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000034933. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37682167 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of an automated template-based treatment planning system for radiotherapy of anal, rectal and prostate cancer.Tech Innov Patient Support Radiat Oncol. 2022 Apr 12;22:30-36. doi: 10.1016/j.tipsro.2022.04.001. eCollection 2022 Jun. Tech Innov Patient Support Radiat Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35464888 Free PMC article.
-
A retrospective study of automatic progressive optimization for lung cancer radiotherapy plans on the Halcyon and RayStation systems.PeerJ. 2025 Aug 5;13:e19831. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19831. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40786101 Free PMC article.
-
Cost analysis of three-dimensional radiation therapy versus intensity-modulated chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced cervical cancer in Peruvian citizens.Ecancermedicalscience. 2023 Apr 20;17:1531. doi: 10.3332/ecancer.2023.1531. eCollection 2023. Ecancermedicalscience. 2023. PMID: 37138970 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment planning comparison of volumetric modulated arc therapy employing a dual-layer stacked multi-leaf collimator and helical tomotherapy for cervix uteri.Radiat Oncol. 2020 Jan 30;15(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s13014-020-1473-z. Radiat Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32000832 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of skin dose in IMRT and VMAT with TrueBeam and Halcyon linear accelerator for whole breast irradiation.Phys Eng Sci Med. 2024 Jun;47(2):443-451. doi: 10.1007/s13246-023-01373-x. Epub 2024 Jan 15. Phys Eng Sci Med. 2024. PMID: 38224383 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Otto K. Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy: IMRT in a single arc. Med Phys. 2008;35:310–317. - PubMed
-
- Bedford JL. Treatment planning for volumetric modulated arc therapy. Med. Phys. 2009;36:5128–38. - PubMed
-
- Andreou M, Karaiskos P, Kordolaimi S. et al. Anatomy-vs. fluence-based planning for prostate cancer treatments using VMAT. Phys Med. 2014;30:202–208. - PubMed
-
- Sharfo AWM, Voet PWJ, Breedveld S. et al. Comparison of VMAT and IMRT strategies for cervical cancer patients using automated planning. Radiother Oncol. 2015;114:395–401. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

