Humanized mice for immune checkpoint blockade in human solid tumors
- PMID: 31763362
- PMCID: PMC6872471
Humanized mice for immune checkpoint blockade in human solid tumors
Abstract
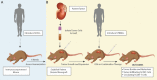
Immunotherapy, specifically research involving immune checkpoint blockers (ICBs), has become a popular trend in anticancer research over the last three years. Due to the difficulties and often poor translation of results from in-vitro models, in-vivo models have become more relevant than ever. With the discovery of NOD, Prkdcscid , and Il2rγ-/- mutations, patient-derived xenograft (PDX) mouse models were developed, providing an ideal environment for ICBs testing. By implanting a PDX with either CD34+ or peripheral blood mononuclear cells, we can create a human immune system capable of mounting a response against tumor burden. These animal models are currently being used to study molecular mechanisms, test drug efficacy, and trial drug combinations. Others have found use for these humanized mouse models as surrogates to represent otherwise uncommon diseases. Limitations remain with regards to what the models are capable of, but in the short amount of time between the development of these models and heightened interest in ICBs, these mice have already shown utility for future developments in the field of immunotherapy.
Keywords: Humanized mice; immune checkpoint blockers; immunotherapy; patient derived xenografts.
AJCEU Copyright © 2019.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Kochanek KD, Murphy SL, Xu J, Arias E. Deaths: final data for 2017. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2019;68:77. - PubMed
-
- Kozlowska AK, Kaur K, Topchyan P, Jewett A. Novel strategies to target cancer stem cells by NK cells; studies in humanized mice. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 2017;22:370–384. - PubMed
-
- Pyo KH, Kim JH, Lee JM, Kim SE, Cho JS, Lim SM, Cho BC. Promising preclinical platform for evaluation of immuno-oncology drugs using Hu-PBL-NSG lung cancer models. Lung Cancer. 2019;127:112–121. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
