Gal-3 is a potential biomarker for spinal cord injury and Gal-3 deficiency attenuates neuroinflammation through ROS/TXNIP/NLRP3 signaling pathway
- PMID: 31763668
- PMCID: PMC6923351
- DOI: 10.1042/BSR20192368
Gal-3 is a potential biomarker for spinal cord injury and Gal-3 deficiency attenuates neuroinflammation through ROS/TXNIP/NLRP3 signaling pathway
Abstract
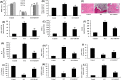
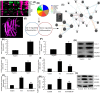
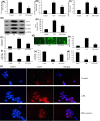
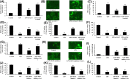
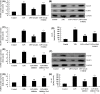
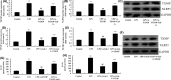
Spinal cord injury (SCI) often occurs in young and middle-aged population. The present study aimed to clarify the function of Galectin-3 (Gal-3) in neuroinflammation of SCI. Sprague-Dawley (SD) rat models with SCI were established in vivo. PC12 cell model in vitro was induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) and Gene chip were used to analyze the expression levels of genes in the signaling pathway. Histological assessment, ELISA and Western blotting were conducted to evaluate the effects of Gal-3 upon the SCI model. In the in vivo SD rat model, Gal-3 expression level was up-regulated. The inhibition of Gal-3 attenuated the neuroinflammation in SCI model. The inhibition of Gal-3 could also mitigate the neuroinflammation and reactive oxygen species (ROS) in in vitro model. ROS reduced the effect of Gal-3 on oxidative stress in in vitro model. Down-regulating the content of TXNIP decreased the effect of Gal-3 on neuroinflammation in in vitro model. Suppressing the level of NLRP3 could weaken the effect of Gal-3 on neuroinflammation in in vitro model. Our data highlight that the Gal-3 plays a vital role in regulating the severity of neuroinflammation of SCI by enhancing the activation of ROS/TXNIP/NLRP3 signaling pathway. In addition, inflammasome/IL-1β production probably acts as the therapeutic target in SCI.
Keywords: Gal-3; NLRP3; ROS; Spinal cord injury; TXNIP.
© 2019 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The present study was approved by the Scientific Review Committee and the Institutional Review Board of the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University.
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Formononetin ameliorates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats by suppressing the ROS-TXNIP-NLRP3 pathway.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020 May 7;525(3):759-766. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.02.147. Epub 2020 Mar 4. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020. PMID: 32145915
-
Ameliorative effects of echinacoside against spinal cord injury via inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome signaling pathway.Life Sci. 2019 Nov 15;237:116978. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116978. Epub 2019 Oct 20. Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31644893
-
FOXO3-induced microRNA-128-3p promotes the progression of spinal cord injury in mice via regulating NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis.Front Immunol. 2025 Feb 21;16:1526721. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1526721. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40061945 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammasome: Its role in traumatic brain and spinal cord injury.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Jul;233(7):5160-5169. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26287. Epub 2018 Jan 19. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29150951 Review.
-
Role of NLRP3 Inflammasome in Post-Spinal-Cord-Injury Anxiety and Depression: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2024 Jan 3;15(1):56-70. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.3c00596. Epub 2023 Dec 18. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38109051 Review.
Cited by
-
Palmitic acid up regulates Gal-3 and induces insulin resistance in macrophages by mediating the balance between KLF4 and NF-κB.Exp Ther Med. 2021 Sep;22(3):1028. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10460. Epub 2021 Jul 18. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 34373714 Free PMC article.
-
New Insight of Circular RNAs' Roles in Central Nervous System Post-Traumatic Injury.Front Neurosci. 2021 Mar 23;15:644239. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.644239. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33841083 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNAs in organ injury: recent development.J Transl Med. 2022 Nov 18;20(1):533. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03725-9. J Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36401311 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glycan-Lectin Interactions in Cancer and Viral Infections and How to Disrupt Them.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 30;22(19):10577. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910577. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34638920 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The NLRP3 inflammasome: contributions to inflammation-related diseases.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2023 Jun 27;28(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s11658-023-00462-9. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2023. PMID: 37370025 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Su Y., Chen Z., Du H., Liu R., Wang W., Li H. et al. . (2019) Silencing miR-21 induces polarization of astrocytes to the A2 phenotype and improves the formation of synapses by targeting glypican 6 via the signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 pathway after acute ischemic spinal cord injury. FASEB J. 33, fj201900743R - PubMed
-
- Zhou Y., Dong Q., Pan Z., Song Y., Su P., Niu Y. et al. . (2019) Hyperbaric oxygen improves functional recovery of the injured spinal cord by inhibiting inflammation and glial scar formation. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehab. 98, 914–920 - PubMed
-
- Wang B., Shen P.F., Qu Y.X., Zheng C., Xu J.D., Xie Z.K. et al. . (2019) miR-940 promotes spinal cord injury recovery by inhibiting TLR4/NF-kappaB pathway-mediated inflammation. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 23, 3190–3197 - PubMed
-
- Lv Z.C., Cao X.Y., Guo Y.X., Zhang X.D., Ding J., Geng J. et al. . (2019) Effects of MiR-146a on repair and inflammation in rats with spinal cord injury through the TLR/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 23, 4558–4563 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

