CRISPR-Cas9-Guided Genome Engineering in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 31763794
- PMCID: PMC6905509
- DOI: 10.1002/cpmb.106
CRISPR-Cas9-Guided Genome Engineering in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
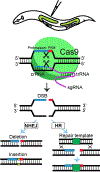
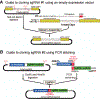
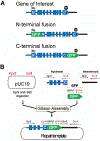
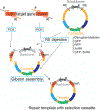
The CRISPR-Cas (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats-CRISPR-associated protein) system is being used successfully for efficient and targeted genome editing in various organisms, including the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Recent studies have developed a variety of CRISPR-Cas9 approaches to enhance genome engineering via two major DNA double-strand break repair pathways: nonhomologous end joining and homologous recombination. Here, we describe a protocol for Cas9-mediated C. elegans genome editing together with single guide RNA (sgRNA) and repair template cloning (canonical marker-free and cassette selection methods), as well as injection methods required for delivering Cas9, sgRNAs, and repair template DNA into the germline. © 2019 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Basic Protocol 1: Guide RNA preparation Alternate Protocol 1: sgRNA cloning using fusion PCR Basic Protocol 2: Preparation of a repair template for homologous recombination Alternate Protocol 2: Preparation of repair template donors for the cassette selection method Basic Protocol 3: Injecting animals Basic Protocol 4: Screening transgenic worms with marker-free method Alternate Protocol 3: Screening transgenic worms with cassette selection method.
Keywords: C. elegans; CRISPR; CRISPR-Cas; Cas9; genome editing; genome engineering.
© 2019 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

