Exophthalmometry values in the Hong Kong Chinese adult population from a population-based study
- PMID: 31764812
- PMCID: PMC6882604
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000017993
Exophthalmometry values in the Hong Kong Chinese adult population from a population-based study
Abstract
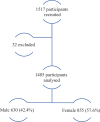
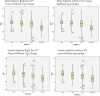
This study aims to establish the range of exophthalmometry values (EV) in the adult Hong Kong (HK) Chinese population, its relationship with various anthropometric parameters, and to compare it with the EV in different ethnic groups.About 1485 adult HK Chinese were drawn from a random sample from the community-based FAMILY Cohort. Participants were interviewed, and comprehensive ophthalmological assessments were conducted. EV was measured using the Hertel's exophthalmometer.EV of both eyes from 630 male (42.4%) and 855 female (57.6%) participants, mean age 54 ± 17.2 and 52 ± 16 respectively were analyzed. The mean EV were found to be 15.3 ± 2.8 mm in the right eye, 15.2 ± 2.9 mm in the left eye for men and 14.4 ± 2.7 mm in the right eye, 14.3 ± 2.7 mm in the left eye for women. There were no differences in the EV between right and left eyes (P > .05). Men had significantly higher EV than women (P < .05) and age was found to be negatively correlated to EV (P < .05). Body height (r = 0.20), weight (r = 0.25), waist (r = 0.11), hip circumference (r = 0.15), body mass index (r = 0.17), interpupillary distance (r = 0.54), and axial length (AL) (r = 0.20) were all found to have statistically significant positive correlations with EV (P < .01). Spherical equivalent was found to have statistically significant negative correlation with EV (P < .01).Our study provides normative data on EV in the HK Chinese population. Height, weight, interpupillary distance, waist, hip circumference, and AL had positive correlations with EV. Spherical equivalent had negative correlation with EV. There was no significant difference in EV between the right and left eye. Age and gender had significant effect on EV.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Determination of exophthalmometry values in the North Indian population.Indian J Ophthalmol. 2022 Aug;70(8):3083-3087. doi: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_489_22. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35918977 Free PMC article.
-
Normative exophthalmometry values in Hispanic individuals.Arch Soc Esp Oftalmol (Engl Ed). 2023 Apr;98(4):199-205. doi: 10.1016/j.oftale.2023.02.002. Epub 2023 Feb 2. Arch Soc Esp Oftalmol (Engl Ed). 2023. PMID: 36738924
-
Normal values of eye position in the Chinese population of Hong Kong.Optom Vis Sci. 1992 Feb;69(2):152-8. doi: 10.1097/00006324-199202000-00009. Optom Vis Sci. 1992. PMID: 1584554 Review.
-
Normal values of hertel exophthalmometry in children, teenagers, and adults from Tehran, Iran.Optom Vis Sci. 2008 Oct;85(10):1012-7. doi: 10.1097/OPX.0b013e3181890dc7. Optom Vis Sci. 2008. PMID: 18832980
-
Parallax-free exophthalmometry: a comprehensive review of the literature on clinical exophthalmometry and the introduction of the first parallax-free exophthalmometer.Orbit. 2015 Feb;34(1):23-9. doi: 10.3109/01676830.2014.963877. Epub 2014 Oct 14. Orbit. 2015. PMID: 25313439 Review.
Cited by
-
Hertel Exophthalmometry Values in a Greek Adult Outpatient Clinic-Based Population: Association With Demographic Factors and Systemic Disease.Cureus. 2023 Feb 15;15(2):e35027. doi: 10.7759/cureus.35027. eCollection 2023 Feb. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 36938254 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of exophthalmometry values in the North Indian population.Indian J Ophthalmol. 2022 Aug;70(8):3083-3087. doi: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_489_22. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35918977 Free PMC article.
-
The study of relationship between ocular biometry and exophthalmometry in adult Malay population of Kelantan, Malaysia.Taiwan J Ophthalmol. 2021 Mar 29;12(1):44-52. doi: 10.4103/tjo.tjo_88_20. eCollection 2022 Jan-Mar. Taiwan J Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 35399980 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of exophthalmos by body mass index for craniofacial reconstruction: consequences for cold cases.Forensic Sci Med Pathol. 2024 Jun;20(2):335-350. doi: 10.1007/s12024-023-00649-8. Epub 2023 Jun 7. Forensic Sci Med Pathol. 2024. PMID: 37280468
References
-
- Farkas LG, Posnick JC, Hreczko TM. Anthropometric growth study of the head. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 1992;29:303–8. - PubMed
-
- Choi KJ, Lee MJ. Comparison of exophthalmos measurements: Hertel exophthalmometer versus orbital parameters in 2-dimensional computed tomography. Can J Ophthalmol 2018;53:384–90. - PubMed
-
- Campi I, Vannucchi GM, Minetti AM, et al. A quantitative method for assessing the degree of axial proptosis in relation to orbital tissue involvement in Graves’ orbitopathy. Ophthalmology 2013;120:1092–8. - PubMed
-
- Leung GM, Ni MY, Wong PT, et al. Cohort profile: FAMILY Cohort. Int J Epidemiol 2017;46:e1. - PubMed
-
- Tsai CC, Kau HC, Kao SC, et al. Exophthalmos of patients with Graves’ disease in Chinese of Taiwan. Eye (Lond) 2006;20:569–73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources