A phase 1, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of single and multiple doses of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate in Japanese and Caucasian healthy adult subjects
- PMID: 31765110
- PMCID: PMC7292221
- DOI: 10.1002/npr2.12082
A phase 1, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of single and multiple doses of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate in Japanese and Caucasian healthy adult subjects
Abstract
Aim: To assess safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate in Japanese and Caucasian healthy adults.
Methods: A phase 1, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, single- and multiple-dose study in Japanese and Caucasian subjects. Subjects received lisdexamfetamine 20 mg or placebo on Day 1, then lisdexamfetamine 20 mg/d (Days 4-8), 50 mg/d (Days 9-13), 70 mg/d (Days 14-18), or matching placebo. Pharmacokinetic parameters for lisdexamfetamine and d-amphetamine were estimated by noncompartmental analysis.
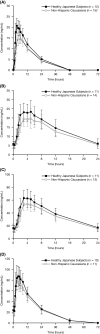
Results: Fifteen Japanese and 19 Caucasian subjects were enrolled and randomized. The lisdexamfetamine and d-amphetamine plasma concentration-time curves were similar for both ethnic groups following single and multiple doses. Mean area under the concentration-time curves for d-amphetamine were higher (by 11%-15%) in Japanese than Caucasian subjects following multiple dosing of lisdexamfetamine. Mean bodyweight was 17% lower in Japanese than Caucasian subjects. Weight-corrected means for oral clearance were similar in both ethnic groups, with no unexpected accumulation of d-amphetamine. Lisdexamfetamine was generally well tolerated by both ethnic groups, with no serious adverse events reported. The 10/12 Japanese and 11/16 Caucasian subjects who received lisdexamfetamine completed the study; two Japanese and three Caucasian subjects discontinued due to adverse events. Most adverse events were of mild severity.
Conclusion: Pharmacokinetics were generally similar for Japanese and Caucasian subjects; the minor differences observed were likely due to bodyweight differences in the two ethnic groups. Lisdexamfetamine was generally well tolerated. Adverse events were consistent with the established safety profile of lisdexamfetamine and were similar in both ethnic groups.
Keywords: attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder; d-amphetamine; lisdexamfetamine dimesylate; pharmacokinetics; psychopharmacology: clinical; safety.
© 2019 Takeda. Neuropsychopharmacology Reports published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of The Japan Society of Neuropsychopharmacology.
Conflict of interest statement
JE is a former employee of Shire. PM and MC are employees of Shire and hold stock and/or stock options in Shire. YM is an employee of Shionogi & Co., Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Population pharmacokinetic and exposure-response analyses of d-amphetamine after administration of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate in Japanese pediatric ADHD patients.Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2020 Dec;35(6):548-554. doi: 10.1016/j.dmpk.2020.08.005. Epub 2020 Sep 18. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2020. PMID: 33082099
-
Pharmacokinetics of Coadministered Viloxazine Extended-Release (SPN-812) and Lisdexamfetamine in Healthy Adults.J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2021 Mar-Apr 01;41(2):155-162. doi: 10.1097/JCP.0000000000001361. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33587403 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of lisdexamfetamine on plasma steroid concentrations compared with d-amphetamine in healthy subjects: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2019 Feb;186:212-225. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2018.10.016. Epub 2018 Oct 28. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30381248 Clinical Trial.
-
Lisdexamfetamine: chemistry, pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, and clinical efficacy, safety, and tolerability in the treatment of binge eating disorder.Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2018 Feb;14(2):229-238. doi: 10.1080/17425255.2018.1420163. Epub 2018 Jan 4. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 29258368 Review.
-
The efficacy and safety profile of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate, a prodrug of d-amphetamine, for the treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children and adults.Clin Ther. 2009 Jan;31(1):142-76. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2009.01.015. Clin Ther. 2009. PMID: 19243715 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of amphetamines on blood pressure.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Mar 28;3(3):CD007896. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007896.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40152309
-
Safety, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of BI 655064 in phase 1 clinical trials in healthy Chinese and Japanese subjects.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2021 Apr;87(4):2000-2013. doi: 10.1111/bcp.14601. Epub 2020 Dec 9. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33047859 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
An Efficient Combination Therapy with Lisdexamfetamine Dimesylate and Topiramate in Improving Binge Eating Scale & Metabolic Profile in Binge Eating Disorder: A Randomized Control Trial.Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 2024 Aug 31;22(3):493-501. doi: 10.9758/cpn.23.1151. Epub 2024 Jun 27. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39069689 Free PMC article.
-
Safety of Stimulants Across Patient Populations: A Meta-Analysis.JAMA Netw Open. 2025 May 1;8(5):e259492. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.9492. JAMA Netw Open. 2025. PMID: 40343695 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Krishnan SM, Stark JG. Multiple daily‐dose pharmacokinetics of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate in healthy adult volunteers. Curr Med Res Opin. 2008;24:33–40. - PubMed
-
- Shire . Elvanse® (lisdexamfetamine dimesylate); 2018. [Cited 11 October 2018]. Available from https://www.shire.com/products/product-list
-
- Boellner SW, Stark JG, Krishnan S, Zhang Y. Pharmacokinetics of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate and its active metabolite, d‐amphetamine, with increasing oral doses of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate in children with attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a single‐dose, randomized, open‐label, crossover study. Clin Ther. 2010;32:252–64. - PubMed
-
- Ermer JC, Adeyi BA, Pucci ML. Pharmacokinetic variability of long‐acting stimulants in the treatment of children and adults with attention‐deficit hyperactivity disorder. CNS Drugs. 2010;24:1009–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources