Cancer Cell Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles for Cancer Management
- PMID: 31766360
- PMCID: PMC6966582
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers11121836
Cancer Cell Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles for Cancer Management
Abstract
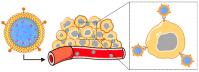
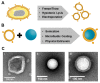
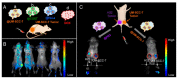
Cancer is a global health problem in need of transformative treatment solutions for improved patient outcomes. Many conventional treatments prove ineffective and produce undesirable side effects because they are incapable of targeting only cancer cells within tumors and metastases post administration. There is a desperate need for targeted therapies that can maximize treatment success and minimize toxicity. Nanoparticles (NPs) with tunable physicochemical properties have potential to meet the need for high precision cancer therapies. At the forefront of nanomedicine is biomimetic nanotechnology, which hides NPs from the immune system and provides superior targeting capabilities by cloaking NPs in cell-derived membranes. Cancer cell membranes expressing "markers of self" and "self-recognition molecules" can be removed from cancer cells and wrapped around a variety of NPs, providing homotypic targeting and circumventing the challenge of synthetically replicating natural cell surfaces. Compared to unwrapped NPs, cancer cell membrane-wrapped NPs (CCNPs) provide reduced accumulation in healthy tissues and higher accumulation in tumors and metastases. The unique biointerfacing capabilities of CCNPs enable their use as targeted nanovehicles for enhanced drug delivery, localized phototherapy, intensified imaging, or more potent immunotherapy. This review summarizes the state-of-the-art in CCNP technology and provides insight to the path forward for clinical implementation.
Keywords: biomimetic; cancer; drug delivery; imaging; immunotherapy; membrane-wrapped; nanocarrier; photodynamic therapy; photothermal therapy; targeted delivery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


References
-
- Lang T., Yin Q., Li Y. Progress of Cell-Derived Biomimetic Drug Delivery Systems for Cancer Therapy. Adv. Ther. 2018;1:1800053. doi: 10.1002/adtp.201800053. - DOI
-
- Sun T., Zhang Y.S., Pang B., Hyun D.C., Yang M., Xia Y. Engineered nanoparticles for drug delivery in cancer therapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014;53:12320–12364. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

