Marine Polysaccharides in Pharmaceutical Applications: Fucoidan and Chitosan as Key Players in the Drug Delivery Match Field
- PMID: 31766498
- PMCID: PMC6950187
- DOI: 10.3390/md17120654
Marine Polysaccharides in Pharmaceutical Applications: Fucoidan and Chitosan as Key Players in the Drug Delivery Match Field
Abstract
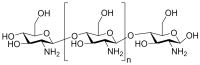
The use of marine-origin polysaccharides has increased in recent research because they are abundant, cheap, biocompatible, and biodegradable. These features motivate their application in nanotechnology as drug delivery systems; in tissue engineering, cancer therapy, or wound dressing; in biosensors; and even water treatment. Given the physicochemical and bioactive properties of fucoidan and chitosan, a wide range of nanostructures has been developed with these polysaccharides per se and in combination. This review provides an outline of these marine polysaccharides, including their sources, chemical structure, biological properties, and nanomedicine applications; their combination as nanoparticles with descriptions of the most commonly used production methods; and their physicochemical and biological properties applied to the design of nanoparticles to deliver several classes of compounds. A final section gives a brief overview of some biomedical applications of fucoidan and chitosan for tissue engineering and wound healing.
Keywords: anticancer compounds; ionic crosslinking method; nanoparticles; polyelectrolyte self-assembly method; polyphenolic compounds.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
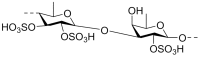
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

