Anthocyanins Potentially Contribute to Defense against Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 31766696
- PMCID: PMC6930593
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24234255
Anthocyanins Potentially Contribute to Defense against Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
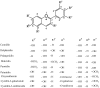
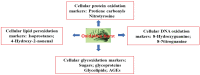
Anthocyanins (ANTs) are plant pigments that belong to a flavanol class of polyphenols and have diverse pharmacological properties. These compounds are primarily found in fruits and vegetables, with an average daily intake of 180 mgd-1 of these compounds in the developed world. ANTs are potent antioxidants that might regulate the free radical-mediated generation of amyloid peptides (Abeta-amyloids) in the brain, which causes Alzheimer's disease (AD). This study presents a literature review of ANTs from different berries and their potential therapeutic value, with particular emphasis on neurodegenerative AD, which owing to oxidative stress. This review also highlights reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation through energy metabolism, nitrogen reactive species, the role of transition metals in generating ROS, and the radical-quenching mechanisms of natural antioxidants, including ANTs. The current status of the bioavailability, solubility, and structure activity relationship of ANTs is discussed herein.
Keywords: anthocyanins; antioxidants; reactive oxygen species; transition metals.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The private funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision for its publication.
Figures


References
-
- Miguel M.G. Anthocyanins: Antioxidants and/or anti-inflammatory activities. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2011;1:7–15.
-
- Castañeda-Ovando A., Pacheco-Hernández M.L., Páez-Hernández M.E., Rodríguez J.A., Galán-Vidal C. Chemical studies of anthocyanins: A review. Food Chem. 2009;113:859–871. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.09.001. - DOI
-
- Ho L., Ferruzzi M.G., Janle E.M., Wang J., Gong B., Chen T.Y., Lobo J., Cooper B., Wu Q.L., Talcott S.T., et al. Identification of brain-targeted bioactive dietary quercetin-3-O-glucuronide as a novel intervention for Alzheimer’s disease. FASEB J. 2013;27:769–781. doi: 10.1096/fj.12-212118. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

