Associations of serum low-density lipoprotein and systolic blood pressure levels with type 2 diabetic patients with and without peripheral neuropathy: systemic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression analysis of observational studies
- PMID: 31767009
- PMCID: PMC6878654
- DOI: 10.1186/s12902-019-0453-5
Associations of serum low-density lipoprotein and systolic blood pressure levels with type 2 diabetic patients with and without peripheral neuropathy: systemic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression analysis of observational studies
Abstract
Background: Compositional abnormalities in lipoproteins and cardiovascular risk factors play an important role in the progression of diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN). This systematic review aimed to estimate the predicting value of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and systolic blood pressure (SBP) level in type-2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients with and without peripheral neuropathy. We also tried to determine whether LDL and SBP are associated with an increased collision risk of DPN.
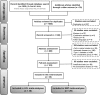
Methods: A systematic search was conducted for eligible publications which explored the LDL and SBP level in T2DM patients with and without peripheral neuropathy. The quality of the included studies was assessed by the QUADAS-2 tool. The standardized mean difference (SMD) with 95% CI of LDL and SBP level were pooled to assess the correlation between LDL and SBP level with DPN. We performed random effects meta-regression analyses to investigate factors associated with an increased collision risk of DPN.
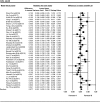
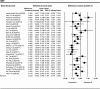
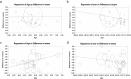
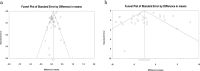
Results: There was a significant association between LDL and SBP with poor prognosis of DPN in those included studies (I2 = 88.1% and I2 = 84.9%, respectively, Both P < 0.001). European T2DM patients have higher serum level of LDL in compare with the European DPN patients (SMD = 0.16, 95% CI: - 0.06 - 0.38; P < 0.001). SBP level was associated with a 2.6-fold decrease in non-DPN patients of T2DM (SMD = - 2.63, 95% CI: - 4.00 - -1.27, P < 0.001). Old age European T2DM patients have significantly high risk for diabetes drivers. Furthermore, the results of the case-control study design model are more precise to show the accuracy of SBP in Asian T2DM patients.
Conclusion: Our finding supports the LDL and SBP status could be associated with increased risk of peripheral neuropathy in T2DM patients.
Keywords: Diabetic peripheral neuropathy; Low-density lipoprotein; Meta-analysis; Meta-regression; Systolic blood pressure; Type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Correlation Analysis and Intervention Study on Disturbance of Lipid Metabolism and Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Feb 22;2022:2579692. doi: 10.1155/2022/2579692. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. Retraction in: Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Jun 28;2023:9830307. doi: 10.1155/2023/9830307. PMID: 35242203 Free PMC article. Retracted. Clinical Trial.
-
The association between pulse wave velocity and peripheral neuropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.J Diabetes Complications. 2017 Nov;31(11):1624-1629. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2017.07.010. Epub 2017 Jul 27. J Diabetes Complications. 2017. PMID: 28893495
-
Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy Is Associated With Higher Systolic Blood Pressure in Adults With Type 2 Diabetes With and Without Hypertension in the Chinese Han Population.Can J Diabetes. 2020 Oct;44(7):615-623. doi: 10.1016/j.jcjd.2019.11.005. Epub 2019 Dec 9. Can J Diabetes. 2020. PMID: 32276832
-
Association between serum uric acid levels and diabetic peripheral neuropathy in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jul 12;15:1416311. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1416311. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39072278 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of the serum lipid profile in prediction of diabetic neuropathy.Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 12;11(1):499. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-79276-0. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33436718 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Hypolipidemic Characteristics of a Methanol Extract of Fermented Green Tea and Spore of Eurotium cristatum SXHBTBU1934 in Golden Hamsters.Nutrients. 2023 Mar 8;15(6):1329. doi: 10.3390/nu15061329. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 36986059 Free PMC article.
-
Immortalized Schwann cell lines as useful tools for pathogenesis-based therapeutic approaches to diabetic peripheral neuropathy.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Jan 21;15:1531209. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1531209. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 39906036 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Features and Rules of Chinese Herbal Medicine in Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy Patients.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Jul 17;2020:5795264. doi: 10.1155/2020/5795264. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 32724325 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomics Analysis Reveals the Effects of Compound Fuzhuan Brick Tea (CFBT) on Regulating Dyslipidemia and Metabolic Disorders in Mice Induced by High-Fat Diet.Nutrients. 2022 Mar 8;14(6):1128. doi: 10.3390/nu14061128. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35334785 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment and external validation of an early warning model of diabetic peripheral neuropathy based on random forest and logistic regression.BMC Endocr Disord. 2024 Sep 20;24(1):196. doi: 10.1186/s12902-024-01728-9. BMC Endocr Disord. 2024. PMID: 39304867 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

