The glutamate receptor GluK2 contributes to the regulation of glucose homeostasis and its deterioration during aging
- PMID: 31767166
- PMCID: PMC6807305
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molmet.2019.09.011
The glutamate receptor GluK2 contributes to the regulation of glucose homeostasis and its deterioration during aging
Abstract
Objective: Islets secrete neurotransmitters including glutamate which participate in fine regulation of islet function. The excitatory ionotropic glutamate receptor GluK2 of the kainate receptor family is widely expressed in brain and also found in islets, mainly in α and γ cells. α cells co-release glucagon and glutamate and the latter increases glucagon release via ionotropic glutamate receptors. However, neither the precise nature of the ionotropic glutamate receptor involved nor its role in glucose homeostasis is known. As isoform specific pharmacology is not available, we investigated this question in constitutive GluK2 knock-out mice (GluK2-/-) using adult and middle-aged animals to also gain insight in a potential role during aging.
Methods: We compared wild-type GluK2+/+ and knock-out GluK2-/- mice using adult (14-20 weeks) and middle-aged animals (40-52 weeks). Glucose (oral OGTT and intraperitoneal IPGTT) and insulin tolerance as well as pyruvate challenge tests were performed according to standard procedures. Parasympathetic activity, which stimulates hormones secretion, was measured by electrophysiology in vivo. Isolated islets were used in vitro to determine islet β-cell electrical activity on multi-electrode arrays and dynamic secretion of insulin as well as glucagon was determined by ELISA.
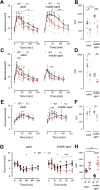
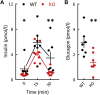
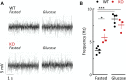
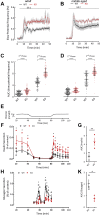
Results: Adult GluK2-/- mice exhibit an improved glucose tolerance (OGTT and IPGTT), and this was also apparent in middle-aged mice, whereas the outcome of pyruvate challenge was slightly improved only in middle-aged GluK2-/- mice. Similarly, insulin sensitivity was markedly enhanced in middle-aged GluK2-/- animals. Basal and glucose-induced insulin secretion in vivo was slightly lower in GluK2-/- mice, whereas fasting glucagonemia was strongly reduced. In vivo recordings of parasympathetic activity showed an increase in basal activity in GluK2-/- mice which represents most likely an adaptive mechanism to counteract hypoglucagonemia rather than altered neuronal mechanism. In vitro recording demonstrated an improvement of glucose-induced electrical activity of β-cells in islets obtained from GluK2-/- mice at both ages. Finally, glucose-induced insulin secretion in vitro was increased in GluK2-/- islets, whereas glucagon secretion at 2 mmol/l of glucose was considerably reduced.
Conclusions: These observations indicate a general role for kainate receptors in glucose homeostasis and specifically suggest a negative effect of GluK2 on glucose homeostasis and preservation of islet function during aging. Our observations raise the possibility that blockade of GluK2 may provide benefits in glucose homeostasis especially during aging.
Keywords: Aging; GRIK2; GluK2; Islets; Kainate receptor; Microelectrode array.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Elsevier GmbH.. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Hayashi M., Morimoto R., Yamamoto A., Moriyama Y. Expression and localization of vesicular glutamate transporters in pancreatic islets, upper gastrointestinal tract, and testis. Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry. 2003;51:1375–1390. - PubMed
-
- Hayashi M., Yamada H., Uehara S., Morimoto R., Muroyama A., Yatsushiro S. Secretory granule-mediated co-secretion of L-glutamate and glucagon triggers glutamatergic signal transmission in islets of Langerhans. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2003;278:1966–1974. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

