Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1)
- PMID: 31767182
- PMCID: PMC6812410
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molmet.2019.09.010
Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1)
Abstract
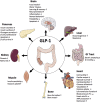
Background: The glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) is a multifaceted hormone with broad pharmacological potential. Among the numerous metabolic effects of GLP-1 are the glucose-dependent stimulation of insulin secretion, decrease of gastric emptying, inhibition of food intake, increase of natriuresis and diuresis, and modulation of rodent β-cell proliferation. GLP-1 also has cardio- and neuroprotective effects, decreases inflammation and apoptosis, and has implications for learning and memory, reward behavior, and palatability. Biochemically modified for enhanced potency and sustained action, GLP-1 receptor agonists are successfully in clinical use for the treatment of type-2 diabetes, and several GLP-1-based pharmacotherapies are in clinical evaluation for the treatment of obesity.
Scope of review: In this review, we provide a detailed overview on the multifaceted nature of GLP-1 and its pharmacology and discuss its therapeutic implications on various diseases.
Major conclusions: Since its discovery, GLP-1 has emerged as a pleiotropic hormone with a myriad of metabolic functions that go well beyond its classical identification as an incretin hormone. The numerous beneficial effects of GLP-1 render this hormone an interesting candidate for the development of pharmacotherapies to treat obesity, diabetes, and neurodegenerative disorders.
Keywords: Diabetes; GLP-1; Glucagon; Incretin; Insulin; Obesity.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Elsevier GmbH.. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Collip J.B. Delayed manifestation of the physiological effects of insulin following the administration of certain pancreatic extracts. American Journal of Physiology. 1923;63:391.
-
- Fisher N.F. Preparation of insulin. American Journal of Physiology. 1923;67:57.
-
- Kimball C., Murlin J. Aqueous extracts of pancreas III. Some precipitation reactions of insulin. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1923;58:337–348.
-
- Muller T.D., Finan B., Clemmensen C., DiMarchi R.D., Tschop M.H. The new biology and pharmacology of glucagon. Physiological Reviews. 2017;97:721–766. - PubMed
-
- Unger R.H., Orci L. Physiology and pathophysiology of glucagon. Physiological Reviews. 1976;56:778–826. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

