Impact and Outcomes of the Oklahoma IDeA Network of Biomedical Research Excellence Summer Undergraduate Research Program
- PMID: 31768211
- PMCID: PMC6853779
- DOI: 10.1128/jmbe.v20i3.1815
Impact and Outcomes of the Oklahoma IDeA Network of Biomedical Research Excellence Summer Undergraduate Research Program
Abstract
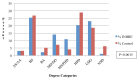
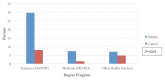
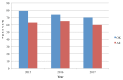
Participating in research under the guidance of faculty mentors can increase undergraduate students' skills, knowledge, and confidence in conducting scientific research and pursing a scientific career. The Oklahoma IDeA Network of Biomedical Research Excellence (OK-INBRE) in the US state of Oklahoma has established an infrastructure to develop future researchers and healthcare professionals by providing students with summer internships. However, long-term benefits have not typically been well quantified, and most prior investigations examining benefits and outcomes of undergraduate summer research experiences have been descriptive and/or observational in nature. To assess OK-INBRE summer program participants, educational and career outcomes were systematically tracked. Data for evaluation included 1) primary sources containing responses to learning surveys from OK-INBRE and national cohorts over a three-year period, and 2) secondary sources from the Oklahoma State Regents for Higher Education (OSRHE), that track educational outcomes of Oklahoma students over a 15-year period. Frequency statistics were compiled and bivariate analyses were conducted to examine participant academic and career outcomes. Survey responses reported higher satisfaction in various dimensions of learning among OK-INBRE students than among corresponding national cohorts, particularly on dimensions of knowledge, skills, and understanding of sciences. The OSRHE data showed that, compared with those in the control group, there was a 100% increase in OK-INBRE participants who enrolled in or had completed a professional degree (e.g., MD/DO) and a 175% increase in students attending a biomedical science graduate program. These findings demonstrate the contribution of the OK-INBRE program in promoting science education and professions.
©2019 Author(s). Published by the American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Building a biomedical pipeline: the impact of the Idaho IDeA INBRE summer research experience at a primarily undergraduate institution.Adv Physiol Educ. 2021 Dec 1;45(4):786-796. doi: 10.1152/advan.00232.2020. Adv Physiol Educ. 2021. PMID: 34529538 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of the Oklahoma IDeA Network of Biomedical Research Excellence research support and mentoring program for early-stage faculty.Adv Physiol Educ. 2022 Sep 1;46(3):443-452. doi: 10.1152/advan.00075.2021. Epub 2022 Jun 6. Adv Physiol Educ. 2022. PMID: 35658613 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of the Impact of the Kansas IDeA Network of Biomedical Research Excellence Program on Undergraduate Participation in Research.J Microbiol Biol Educ. 2013 May 6;14(1):47-57. doi: 10.1128/jmbe.v14i1.492. Print 2013. J Microbiol Biol Educ. 2013. PMID: 23858353 Free PMC article.
-
Using focused ethnography to inform biomedical research infrastructure enhancement at primarily undergraduate institutions.Adv Physiol Educ. 2024 Mar 1;48(1):3-11. doi: 10.1152/advan.00014.2022. Epub 2023 Oct 26. Adv Physiol Educ. 2024. PMID: 37883733 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of summer programmes on the outcomes of disadvantaged or 'at risk' young people: A systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2024 Jun 13;20(2):e1406. doi: 10.1002/cl2.1406. eCollection 2024 Jun. Campbell Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38873396 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
NIH funding trends to US medical schools from 2009 to 2018.PLoS One. 2020 Jun 1;15(6):e0233367. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0233367. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32480400 Free PMC article.
-
Outcomes of the UAMS summer undergraduate research program to increase diversity in research and health professions.Adv Physiol Educ. 2023 Mar 1;47(1):20-25. doi: 10.1152/advan.00201.2022. Epub 2022 Nov 3. Adv Physiol Educ. 2023. PMID: 36326474 Free PMC article.
-
Building a biomedical pipeline: the impact of the Idaho IDeA INBRE summer research experience at a primarily undergraduate institution.Adv Physiol Educ. 2021 Dec 1;45(4):786-796. doi: 10.1152/advan.00232.2020. Adv Physiol Educ. 2021. PMID: 34529538 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Centers of Biomedical Research Excellence (CoBRE) Grants to Build Research Capacity in Underrepresented States.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 9:2023.08.02.551624. doi: 10.1101/2023.08.02.551624. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: FASEB J. 2024 Mar 31;38(6):e23560. doi: 10.1096/fj.202301610R. PMID: 37577479 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Comparing undergraduate research experiences before, during, and after the COVID-19 quarantine: The successful adaptation of the BUILD PODER Summer JumpStart program.PLoS One. 2023 Dec 28;18(12):e0295901. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0295901. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 38153932 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hathaway RS, Nagda BA, Gregerman SR. The relationship of undergraduate research participation to graduate and professional education pursuit: an empirical study. J Coll Stud Dev. 2002;43:614–631.
-
- Harsh JA, Maltese AV, Tai RH. A perspective of gender differences in chemistry and physics undergraduate research experiences. J Chem Educ. 2012;89:1364–1370. doi: 10.1021/ed200581m. - DOI
-
- Hunter AB, Laursen SL, Seymour E. Becoming a scientist: the role of undergraduate research in students’ cognitive, personal, and professional development. Sci Educ. 2007;91:36–74. doi: 10.1002/sce.20173. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

