Atrial Myopathy
- PMID: 31768479
- PMCID: PMC6872845
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2019.05.005
Atrial Myopathy
Abstract
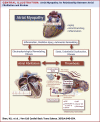
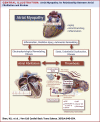
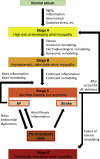
This paper discusses the evolving concept of atrial myopathy by presenting how it develops and how it affects the properties of the atria. It also reviews the complex relationships among atrial myopathy, atrial fibrillation (AF), and stroke. Finally, it discusses how to apply the concept of atrial myopathy in the clinical setting-to identify patients with atrial myopathy and to be more selective in anticoagulation in a subset of patients with AF. An apparent lack of a temporal relationship between episodes of paroxysmal AF and stroke in patients with cardiac implantable electronic devices has led investigators to search for additional factors that are responsible for AF-related strokes. Multiple animal models and human studies have revealed a close interplay of atrial myopathy, AF, and stroke via various mechanisms (e.g., aging, inflammation, oxidative stress, and stretch), which, in turn, lead to fibrosis, electrical and autonomic remodeling, and a pro-thrombotic state. The complex interplay among these mechanisms creates a vicious cycle of ever-worsening atrial myopathy and a higher risk of more sustained AF and strokes. By highlighting the importance of atrial myopathy and the risk of strokes independent of AF, this paper reviews the methods to identify patients with atrial myopathy and proposes a way to incorporate the concept of atrial myopathy to guide anticoagulation in patients with AF.
Keywords: 4D, 4 dimensional; AF, atrial fibrillation; APD, action potential duration; CMR, cardiac magnetic resonance; CRP, C-reactive protein; Ca2+, calcium; Cx, connexin; GDF, growth differentiation factor; IL, interleukin; K+, potassium; LA, left atrial; LAA, left atrial appendage; NADPH, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; NOX2, catalytic, membrane-bound subunit of NADPH oxidase; NT-proBNP, N-terminal pro B-type natriuretic peptide; OAC, oral anticoagulant; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TGF, transforming growth factor; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; atrial fibrillation; atrial myopathy; electrophysiology; thrombosis.
© 2019 The Authors.
Figures

References
-
- McGrath E.R., Kapral M.K., Fang J. Association of atrial fibrillation with mortality and disability after ischemic stroke. Neurology. 2013;81:825–832. - PubMed
-
- Van Gelder I.C., Hagens V.E., Bosker H.A. A comparison of rate control and rhythm control in patients with recurrent persistent atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:1834–1840. - PubMed
-
- Wyse D.G., Waldo A.L., DiMarco J.P. A comparison of rate control and rhythm control in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:1825–1833. - PubMed
-
- Brambatti M., Connolly S.J., Gold M.R. Temporal relationship between subclinical atrial fibrillation and embolic events. Circulation. 2014;129:2094–2099. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

